The Yeoman Test is a clinical examination maneuver used to assess sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pathology and anterior sacroiliac ligament involvement. It may also elicit pain from pathology affecting the hip joint or the lumbar spine, so interpretation must be made cautiously and in the context of a full musculoskeletal assessment.
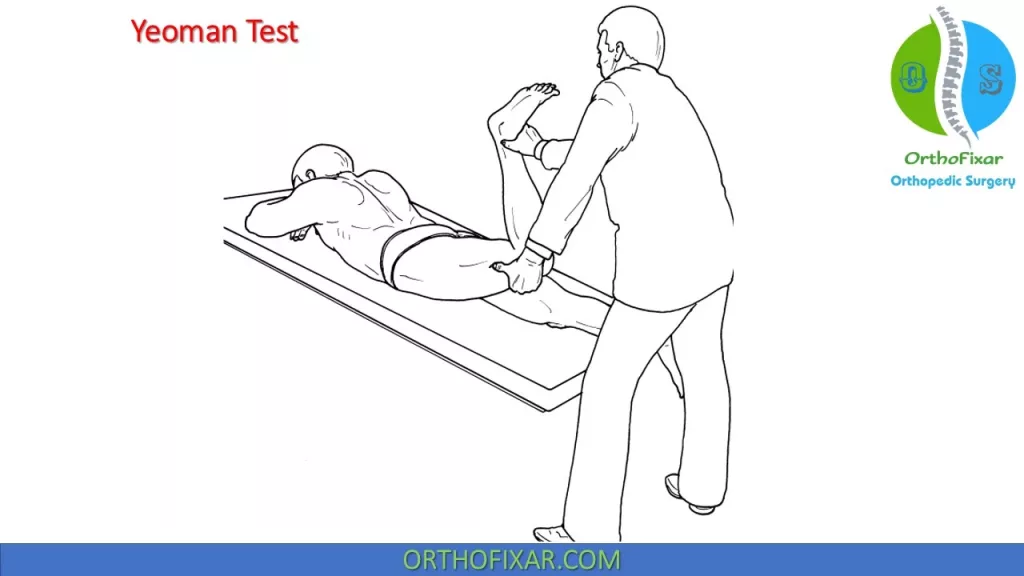
How is the Yeoman Test Performed?
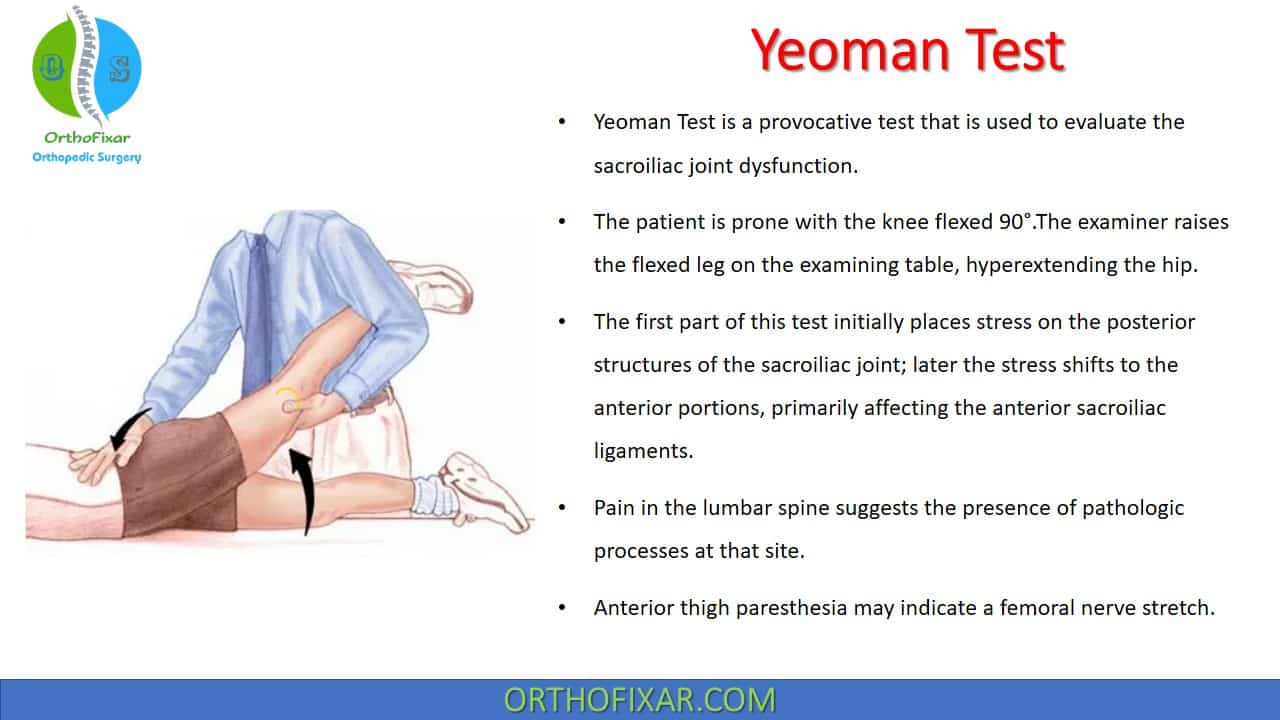
- The patient lies prone on the examination table.
- The examiner stabilizes the ipsilateral pelvis by applying downward pressure over the sacroiliac joint.
- The examiner then flexes the patient’s knee to 90° and extends the hip by lifting the thigh off the table.
- The test is performed bilaterally for comparison.
What does a positive Yeoman Test mean?
The first part of this test initially places stress on the posterior structures of the sacroiliac joint; later the stress shifts to the anterior portions, primarily affecting the anterior sacroiliac ligaments.
- Pain over the sacroiliac area suggests anterior sacroiliac ligament pathology or sacroiliitis.
- Pain in the lumbar spine suggests lumbar facet joint involvement.
- Pain localized to the anterior thigh or hip region may indicate hip joint pathology or rectus femoris tightness.
- Anterior thigh paresthesia may indicate a femoral nerve stretch.
Sensitivity & Specificity
- Sensitivity: 93 %
- Specificity: 89 %
Another study by Parisa Nejati to assess the reliability and validity of motion palpation and pain provocation compared with sacroiliac joint (SIJ) block as the gold-standard assessment method of patients with sacroiliac joint dysfunction (SIJD), he found the sensitivity was (64.1%) and specificity was (33.3 %) for Yeoman Test.
Notes
Other structures that are stressed with this maneuver include the lumbar spine, the hip joint, and the iliopsoas muscle.
The Yeoman Test helps differentiate between sacroiliac, hip, and lumbar sources of low back pain. It is often performed alongside other SIJ stress tests such as the Gaenslen test, FABER (Patrick’s) test, and Thigh Thrust test to improve diagnostic reliability.
Reference
- Laslett M, Young SB, Aprill CN, McDonald B. Diagnosing painful sacroiliac joints: A validity study of a McKenzie evaluation and sacroiliac provocation tests. Aust J Physiother. 2003;49(2):89-97. doi: 10.1016/s0004-9514(14)60125-2. PMID: 12775204. PubMed
- Laslett M, Aprill CN, McDonald B, Young SB. Diagnosis of sacroiliac joint pain: validity of individual provocation tests and composites of tests. Man Ther. 2005 Aug;10(3):207-18. doi: 10.1016/j.math.2005.01.003. PMID: 16038856. PubMed
- Nejati P, Sartaj E, Imani F, Moeineddin R, Nejati L, Safavi M. Accuracy of the Diagnostic Tests of Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction. J Chiropr Med. 2020 Mar;19(1):28-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jcm.2019.12.002. Epub 2020 Sep 12. PMID: 33192189; PMCID: PMC7646135. PubMed
- Clinical Tests for the Musculoskeletal System 3rd Edition.
- Dutton’s Orthopaedic Examination, Evaluation, And Intervention 3rd Edition.