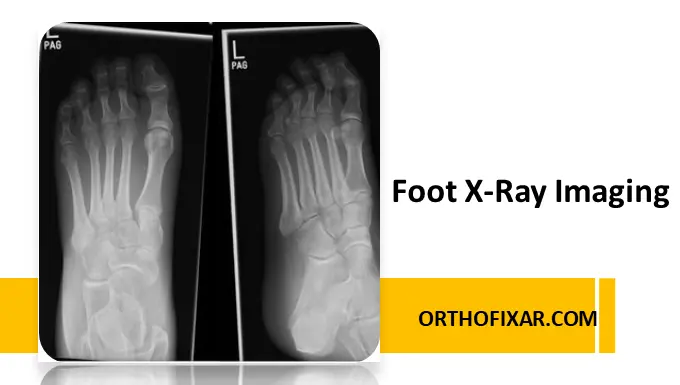
Foot X-Ray imaging is a fundamental diagnostic tool in musculoskeletal radiology. It is routinely used to evaluate traumatic injuries, degenerative conditions, infections, congenital abnormalities, and alignment disorders of the foot. Accurate positioning and appropriate selection of X-ray views are essential for optimal visualization of the bones, joints, and soft tissue interfaces of the foot.
Anatomy Overview Relevant to Foot X-Ray
The foot consists of:
- Hindfoot: Talus and calcaneus
- Midfoot: Navicular, cuboid, and three cuneiform bones
- Forefoot: Metatarsals and phalanges
Foot X-ray imaging aims to assess bone integrity, joint spaces, alignment, and secondary soft tissue signs such as swelling or calcifications.
See Also: Foot Anatomy
Standard Foot X-Ray Imaging Positions
1. Dorsoplantar (Anteroposterior) View of the Foot
Positioning
- The patient is seated or supine
- The plantar surface of the foot rests flat on the image receptor
- The central X-ray beam is angled approximately 10° posteriorly toward the base of the third metatarsal
Structures Best Visualized
- Metatarsals and phalanges
- Tarsometatarsal joints
- Overall forefoot alignment
Indications
- Suspected metatarsal or phalangeal fractures
- Hallux valgus and bunion deformities
- Degenerative joint disease
- Lisfranc joint injuries
See Also: Ankle X-Ray Imaging
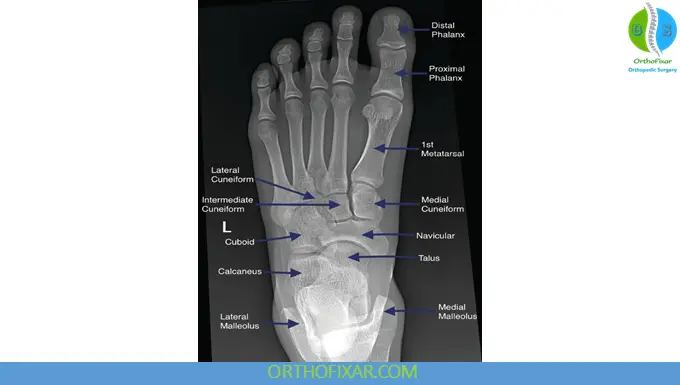
2. Oblique View of the Foot (Medial Oblique)
Positioning
- The foot is rotated medially approximately 30–45°
- The plantar surface remains in contact with the receptor
Structures Best Visualized
- Cuboid and navicular bones
- Calcaneocuboid joint
- Intermetatarsal spaces
Indications
- Subtle fractures of the midfoot
- Tarsal coalition
- Evaluation of joint spaces not clearly seen on AP view
- Foreign body detection
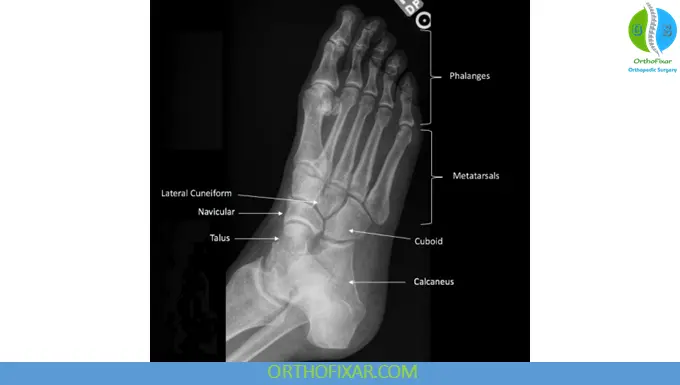
3. Lateral View of the Foot
Positioning
- The patient lies on the affected side
- The foot is positioned laterally with toes dorsiflexed
- The beam is centered over the medial cuneiform
Structures Best Visualized
- Calcaneus, talus, and longitudinal arch
- Talocalcaneal and talonavicular joints
Indications
- Heel pain and calcaneal fractures
- Flatfoot or pes cavus deformities
- Plantar fasciitis (heel spur assessment)
- Evaluation of arch integrity
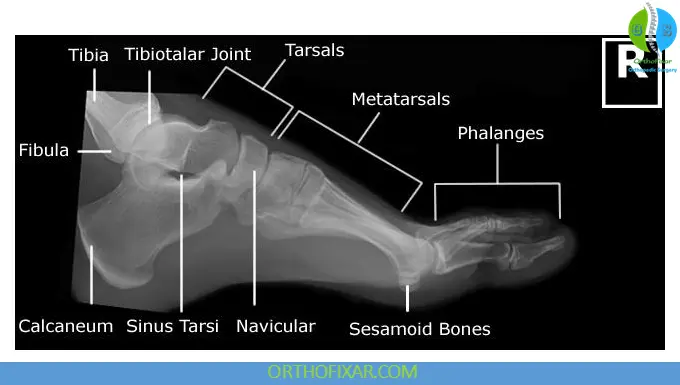
4. Weight-Bearing Foot X-Ray (AP and Lateral)
Positioning
- The patient stands with full weight distributed evenly on the foot
- Images may be obtained bilaterally for comparison
Structures Best Visualized
- Joint alignment under physiological load
- Longitudinal and transverse arches
Indications
- Flatfoot or high-arch deformities
- Hallux valgus severity assessment
- Degenerative arthritis
- Preoperative and postoperative evaluation
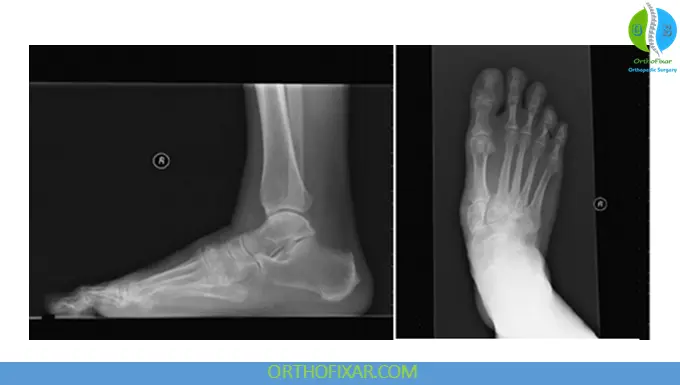
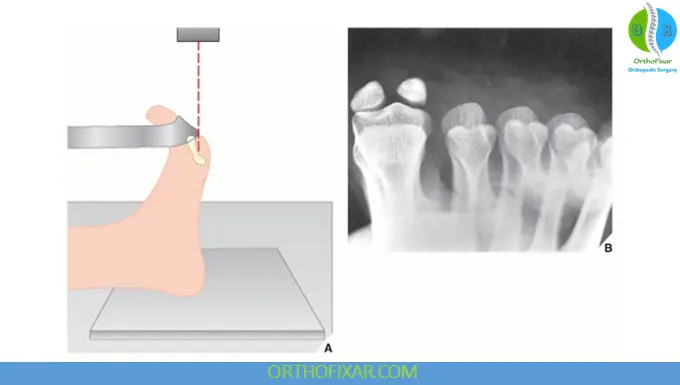
5. Sesamoid View (Tangential Projection)
Positioning
- The toes are dorsiflexed
- The beam is angled tangentially to the first metatarsophalangeal joint
Structures Best Visualized
- Medial and lateral sesamoid bones
Indications
- Sesamoid fractures
- Sesamoiditis
- Chronic forefoot pain beneath the first metatarsal head
Clinical Indications for Foot X-Ray Imaging
Foot X-rays are indicated in a wide range of clinical scenarios, including:
- Acute trauma: fractures, dislocations, crush injuries
- Chronic pain: stress fractures, arthritis
- Infection: osteomyelitis, diabetic foot complications
- Congenital and developmental disorders
- Alignment abnormalities: pes planus, pes cavus
- Pre- and post-surgical assessment
Radiation Safety Considerations
Although foot X-rays involve low radiation exposure, proper collimation, shielding when appropriate, and adherence to the ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) principle remain essential, particularly in pediatric patients.
References & More
- Pearse EO, Klass B, Bendall SP. The ‘ABC’ of examining foot radiographs. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2005 Nov;87(6):449-51. doi: 10.1308/003588405X51119. PMID: 16263015; PMCID: PMC1964112. Pubmed
- Lamm BM, Stasko PA, Gesheff MG, Bhave A. Normal Foot and Ankle Radiographic Angles, Measurements, and Reference Points. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2016 Sep-Oct;55(5):991-8. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2016.05.005. Epub 2016 Jun 16. PMID: 27320694. Pubmed
- Li J, Zhong Z, Lidtke R, Kuettner KE, Peterfy C, Aliyeva E, Muehleman C. Radiography of soft tissue of the foot and ankle with diffraction enhanced imaging. J Anat. 2003 May;202(5):463-70. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2003.00175.x. PMID: 12739623; PMCID: PMC1571096. Pubmed
- Orthopedic Physical Assessment by David J. Magee, 7th Edition.