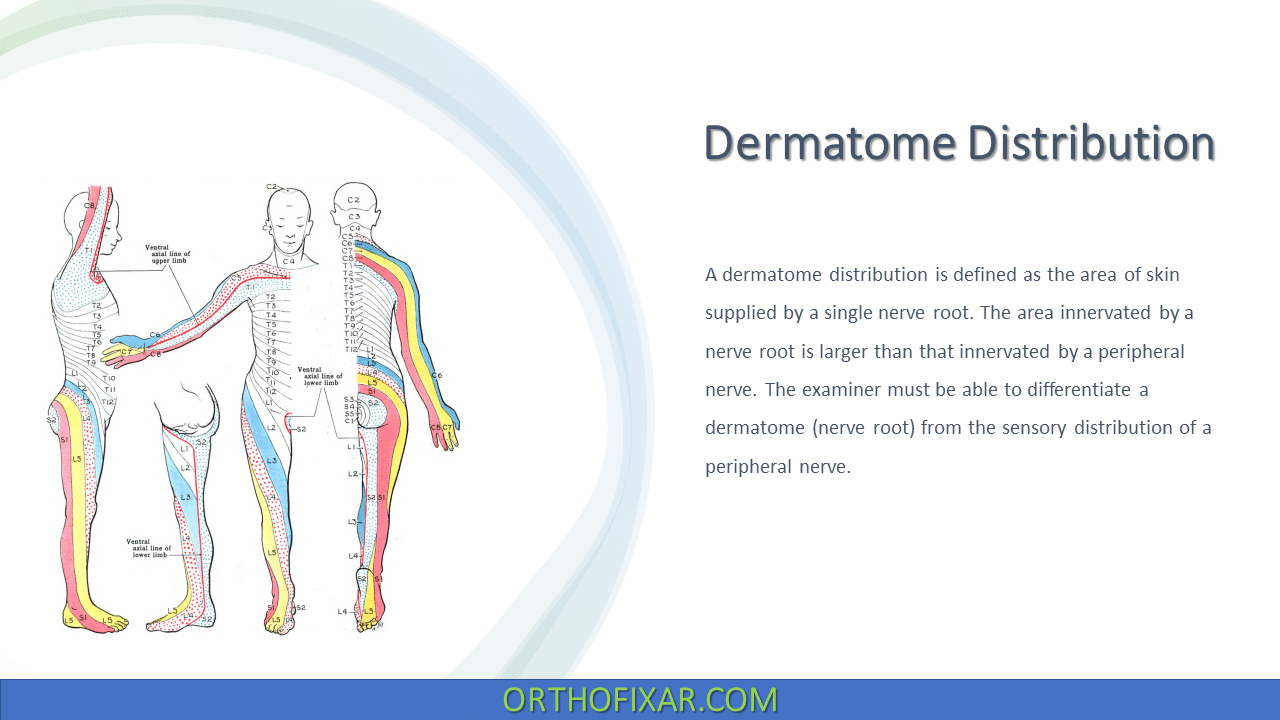
A dermatome distribution is defined as the area of skin supplied by a single nerve root. The area innervated by a nerve root is larger than that innervated by a peripheral nerve. The examiner must be able to differentiate a dermatome (nerve root) from the sensory distribution of a peripheral nerve.
Nerve roots are made up of anterior (ventral) and posterior (dorsal) portions that unite near or in the intervertebral foramen to form a single nerve root or spinal nerve. They are the most proximal parts of the peripheral nervous system. The sensory distribution of each nerve root is called the dermatome.
The human body has 31 nerve root pairs:
- 8 cervical,
- 12 thoracic,
- 5 lumbar,
- 5 sacral,
- 1 coccygeal.
Slight differences and variabilities occur with each patient and dermatomes also exhibit a great deal of overlap. The variability in dermatomes was aptly demonstrated by Keegan and Garrett in 1948. The overlap may be demonstrated by the fact that, in the thoracic spine, the loss of one dermatome often goes unnoticed because of the overlap of the adjacent dermatomes.
See Also: Reflex Testing
Dermatomes of Upper Limb (Cervical)
The upper limb dermatomes arise from C5 to T1 nerve roots. These roots form the brachial plexus, which distributes sensory supply across the arm, forearm, and hand.
| Nerve Root | Dermatome |
|---|---|
| C1 nerve root | Vertex of skull |
| C2 nerve root | Temple, forehead, occiput |
| C3 nerve root | Entire neck, posterior cheek, temporal area, prolongation forward under mandible |
| C4 nerve root | Shoulder area, clavicular area, upper scapular area |
| C5 nerve root | Deltoid area, anterior aspect of entire arm to base of thumb |
| C6 nerve root | Anterior arm, radial side of hand to thumb and index finger |
| C7 nerve root | Lateral arm and forearm to index, long, and ring fingers |
| C8 nerve root | Medial arm and forearm to long, ring, and little fingers |

C5
- Covers the lateral upper arm and shoulder.
- Assessed clinically at the deltoid patch.
- Commonly affected in C5 radiculopathy (e.g., cervical foraminal stenosis).
C6
- Extends down the lateral arm and forearm to the thumb.
- Known as the “thumb dermatome”.
- Weakness often appears in wrist extension in associated radiculopathies.
C7
- Central posterior forearm and the middle finger.
- C7 is the most commonly compressed cervical root.
C8
- Medial forearm and ring/little fingers.
- Symptoms include paresthesia and difficulty with finger flexion.
T1
- Medial elbow area and upper medial forearm.
- Often affected in lower brachial plexus injuries.
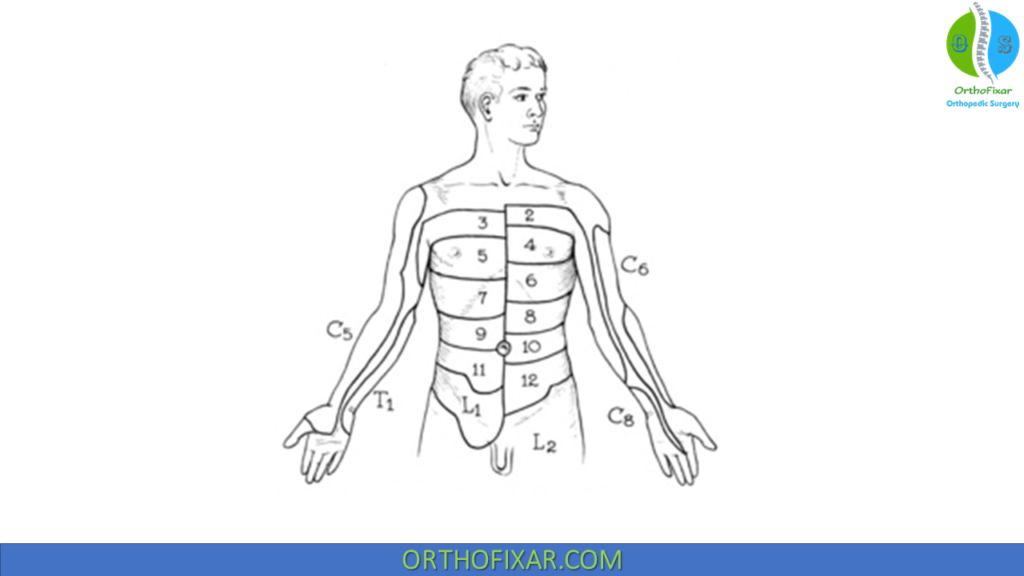
Trunk Dermatomes
| Nerve Root | Dermatome |
|---|---|
| T1 nerve root | Medial side of forearm to base of little finger |
| T2 nerve root | Medial side of upper arm to medial elbow, pectoral and midscapular areas |
| T3–T6 nerve roots | Upper thorax |
| T5–T7 nerve roots | Costal margin |
| T8–T12 nerve roots | Abdomen and lumbar region |
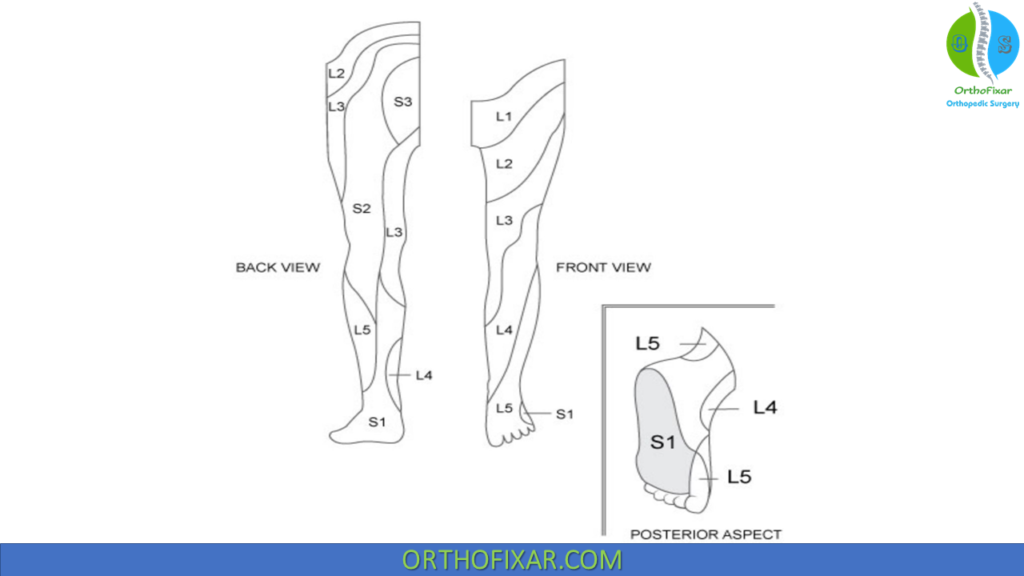
Dermatomes of Lower Limb
The lower limb receives sensory supply mostly from L1–S2. These roots are vital for diagnosing lumbar disc herniation and peripheral neuropathies.
| Nerve Root | Dermatome |
|---|---|
| L1 nerve root | Back, over trochanter and groin |
| L2 nerve root | Back, front of thigh to knee |
| L3 nerve root | Back, upper buttock, anterior thigh and knee, medial lower leg |
| L4 nerve root | Medial buttock, lateral thigh, medial leg, dorsum of foot, big toe |
| L5 nerve root | Buttock, posterior and lateral thigh, lateral aspect of leg, dorsum of foot, medial half of sole, first, second, and third toes |
| S1-S2 nerve roots | Buttock, thigh, and leg posterior |
| S3 nerve root | Groin, medial thigh to knee |
| S4 nerve root | Perineum, genitals, lower sacrum |
See Also: S1 Nerve Root Examination
See Also: Lumbar Spine Nerve Roots
L1
- Covers the inguinal and upper anterior thigh.
- Pain here may signal upper lumbar nerve irritation.
L2
- Involves anterior mid-thigh.
- Tested during hip flexion and sensory palpation.
L3
- Medial thigh and medial knee.
- Commonly affected by L3 disc pathology.
L4
- Medial leg and medial malleolus.
- Known as the “knee-to-ankle medial strip”.
- Loss of patellar reflex suggests L3–L4 involvement.
L5
- Lateral leg and dorsum of the foot, especially the big toe.
- Most frequently involved in lumbar disc herniation (L4–L5).
S1
- Lateral foot and sole, including the little toe.
- Achilles tendon reflex loss indicates S1 dysfunction.
S2
- Posterior thigh and upper calf.
- Often affected in sciatic nerve disorders.
Dermatomes Testing
Dermatome Testing is performed with a pin and cotton wool. Ask the patient to close their eyes and give the feedback regarding the various stimuli. Testing should be done on specific dermatomes and should be compared to bilaterally.
- Light Touch Test: Light Touch Sensation – Dab a piece of cotton wool on an area of skin.
- Pinprick Test: Pain Sensation – Gently touches the skin with the pin ask the patient whether it feels sharp or blunt.
References & More
- Baglien P, Varacallo M. Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Cutaneous Innervation. [Updated 2023 Jul 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545249/
- Whitman PA, Launico MV, Adigun OO. Anatomy, Skin, Dermatomes. [Updated 2023 Oct 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535401/
- Orthopedic Physical Assessment by David J. Magee, 7th Edition.
- Dermatomes – Physiopedia


Closed.