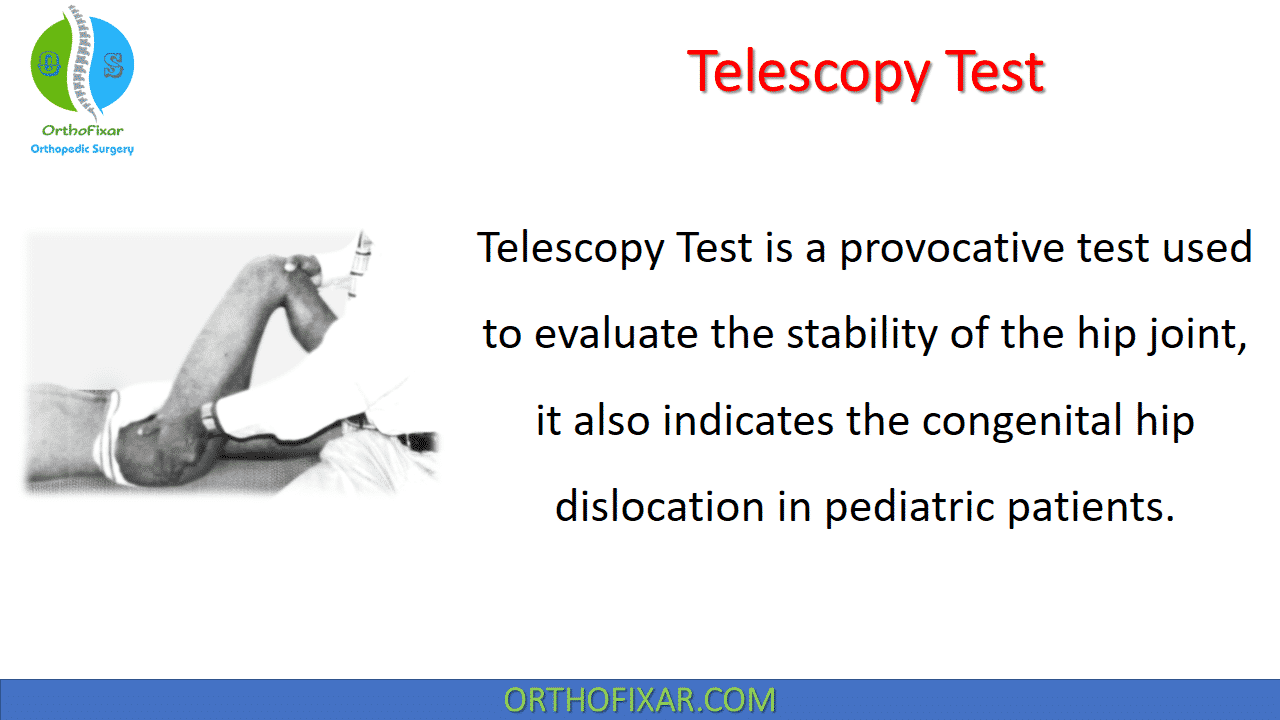
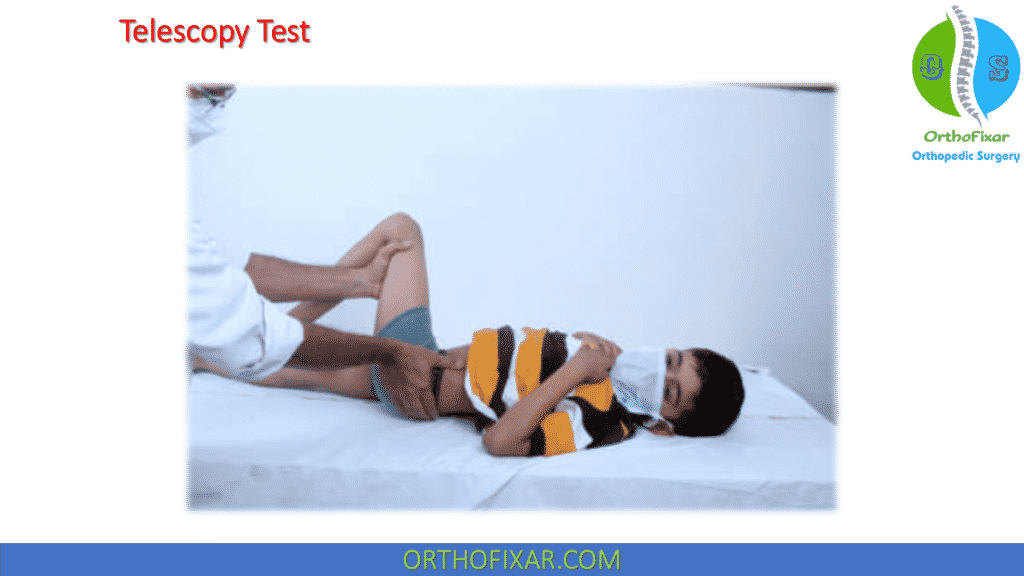
Telescopy Test is an important clinical orthopedic examination used to evaluate the stability of the hip joint most commonly in conditions such as Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH). This physical test helps examiners detect abnormal movement of the femoral head within the acetabulum and is especially useful in pediatric and orthopedic evaluations. It’s also known as the piston test.
This test is most commonly applied in:
- Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)
- Congenital hip dislocation
- Post-traumatic or post-surgical hip instability (less commonly)
How do you perform the Hip Telescopy Test?
- The patient is positioned supine on the examination table, and this is better done with the examiner standing on the side that is to be examined.
- The hip and knee are flexed to 90° and the hip kept in mild adduction.
- The pelvis is supported with one hand by placing the thenar eminence over the anterior superior iliac spine ASIS and the fingers on the greater trochanter.
- The knee/ distal thigh is held with the other hand, and a gentle push and pull force is applied along the long axis of the thigh.
- The examiner assesses the vertical movement of the femur relative to the pelvis.
The hip and knee should have flexion range of movement; adduction should be possible at hip, firm mattress, ideally a painless hip.
See Also:

What does a positive Telescopy Test mean?
A positive telescopy test is indicated by:
- Apparent limb shortening that corrects with traction
- Excessive up-and-down movement of the femur
- A sensation of the femoral head sliding in and out of the acetabulum
When the excursion is more than that compared to the other side, think of conditions like a femoral neck fracture nonunion, hip dislocation, old unreduced posterior hip dislocation, dislocated total hip replacement.
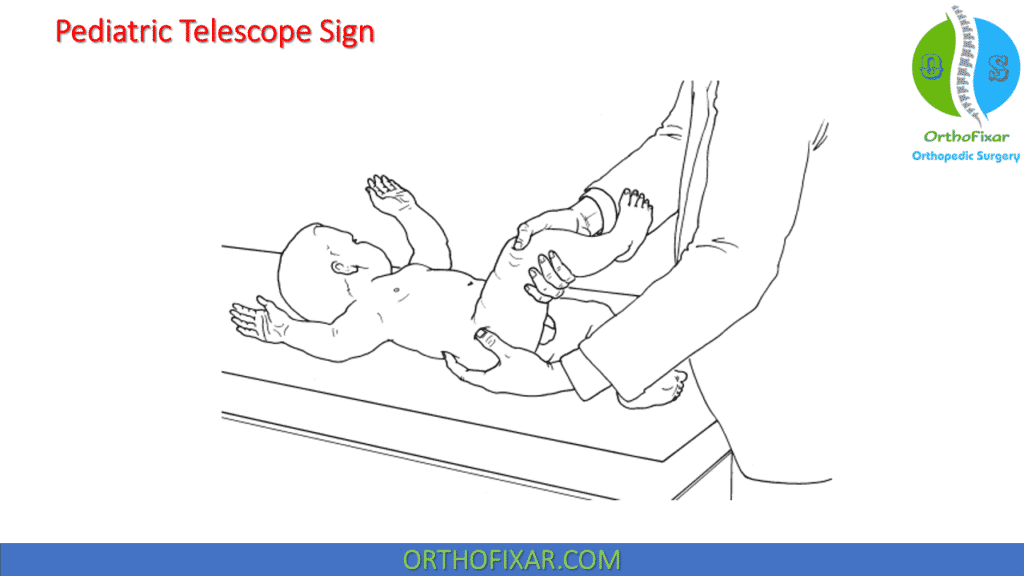
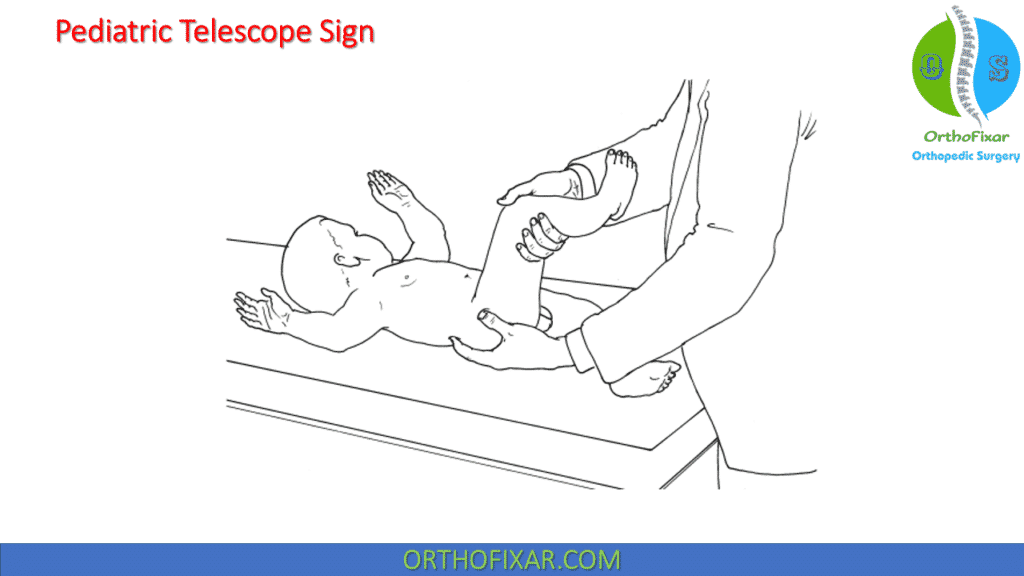
Pediatric Telescope Sign
The Pediatric Telescope Sign indicates the congenital hip dislocation in pediatric patients. It’s performed as following:
The examiner grasps the affected leg with one hand and passively flexes the hip and knee. The other hand rests posterolateral to the hip. The examiner palpates the greater trochanter with the thumb of this hand and the motion of the femoral head with the index finger. The hand guiding the leg alternately applies axial compression and traction to the femur.
In a hip dislocation, the leg will appear to shorten or lengthen. The palpating hand follows the motion of the greater trochanter and femoral head into the dislocated position and back to reduction.
What are the causes of a telescoping hip?
Telescoping hip (positive Telescopy Test) can be caused by multiple conditions:
- Girdlestone arthroplasty.
- Old unreduced dislocation with lax structures.
- Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH).
- Pathological dislocation e.g. TB.
- Charcot’s joint.
- Perthes disease.
- Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE) .
- Squeal of septic arthritis.
- Osteonecrosis with collapse.
- TB hip: Mortar and pestle type, destroyed head, wandering acetabulum.
- Non Union fracture neck femur.
- Non Union fracture intertrochanteric.
Telescopy Test vs Other Hip Tests
| Test | Primary Use |
|---|---|
| Ortolani Test | Detects reducible hip dislocation in infants |
| Barlow Test | Identifies unstable hips prone to dislocation |
| Telescopy Test | Assesses vertical instability and limb shortening |
| Galeazzi Sign | Detects limb length discrepancy |
References
- Clinical Tests for the Musculoskeletal System 3rd Edition.
- Sarvdeep S. Dhatt, Sharad Prabhakar – Handbook of Clinical Examination in Orthopedics. An Illustrated Guide-Springer Singapore.
- Clinical Assessment and Examination in Orthopedics, 2nd Edition Book.
- The video from Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=93pOrTcuiT4