Overview
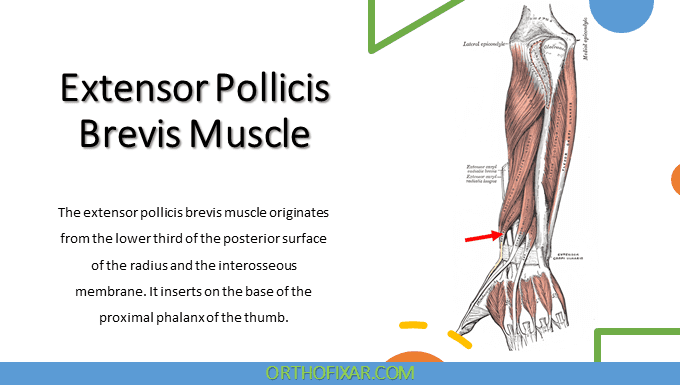
The extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) is a short, fusiform muscle of the posterior compartment of the forearm. It plays a key role in thumb extension and contributes to movements of the wrist. Along with the abductor pollicis longus (APL), it forms the lateral boundary of the anatomical snuff box, an important surface landmark of the wrist.
The muscle belly of the extensor pollicis brevis lies distal to the abductor pollicis longus and is partially covered by it. Its tendon runs parallel and medial to the APL tendon and extends further distally to reach the thumb.
Extensor Pollicis Brevis Muscle Anatomy
Extensor Pollicis Brevis Origin and Insertion
- Origin: Lower third of the posterior surface of the radius and the adjacent interosseous membrane
- Insertion: Base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb
This anatomical arrangement allows the EPB to act primarily on the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint of the thumb.

Innervation
The extensor pollicis brevis is innervated by the posterior interosseous nerve, a deep branch of the radial nerve.
- Nerve: Posterior interosseous nerve
- Root value: C7–C8
Blood Supply
The blood supply of the extensor pollicis brevis comes from the:
- Posterior interosseous artery,
a branch of the common interosseous artery, which arises from the ulnar artery.
Actions of Extensor Pollicis Brevis
The primary and secondary actions of the EPB muscle include:
- Extension of the proximal phalanx of the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal joint
- Assists in extension of the first metacarpal
- Contributes to wrist extension and abduction when acting synergistically with other thumb extensors
When the MCP joint is fixed by antagonistic muscles, the EPB helps stabilize and extend the thumb during functional hand movements.
See Also: Forearm Muscles Anatomy & Function
Anatomical Snuff Box
When the thumb is fully extended, a triangular depression known as the anatomical snuff box becomes visible on the radial aspect of the wrist.
Boundaries:
- Medial: Tendon of extensor pollicis longus (EPL)
- Lateral: Tendons of extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) and abductor pollicis longus (APL)
Floor:
- Scaphoid and trapezium bones
The radial artery passes obliquely through the floor of the snuff box as it travels from the anterior to the dorsal aspect of the hand.

Clinical Relevance
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
Inflammation of the tendons of the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus results in De Quervain’s tenosynovitis, a common cause of radial-sided wrist pain.
- Pain is aggravated by thumb movement and gripping
- Swelling may be present over the anatomical snuff box
Finkelstein Test
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis can be clinically assessed using the Finkelstein test, which reproduces pain by stretching the EPB and APL tendons.
Palpation of Extensor Pollicis Brevis
To test and palpate the extensor pollicis brevis:
- Ask the patient to extend the thumb against resistance at the MCP joint
- A normally functioning EPB tendon becomes visible and palpable:
- On the lateral side of the anatomical snuff box
- Medial to the tendon of the abductor pollicis longus
Summary Table: Extensor Pollicis Brevis
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Muscle | Extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) |
| Origin | Posterior surface of radius and interosseous membrane |
| Insertion | Base of proximal phalanx of thumb |
| Innervation | Posterior interosseous nerve (C7–C8) |
| Blood Supply | Posterior interosseous artery |
| Action | Extends thumb at MCP joint; assists wrist extension |
| Clinical relevance | De Quervain’s tenosynovitis |
Related Anatomy
- Forearm Muscles Anatomy & Function
- Wrist and Hand Examination
- Extensor Pollicis Longus Muscle
- Abductor Pollicis Longus Muscle
References & More
- Cael, C. (2010). Functional anatomy: Musculoskeletal anatomy, kinesiology, and palpation for manual therapists. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins.
- Moore, K. L., Dalley, A. F., & Agur, A. M. R. (2014). Clinically Oriented Anatomy (7th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- Clinically Oriented Anatomy – 8th Edition
- Jabir S, Lyall H, Iwuagwu FC. The extensor pollicis brevis: a review of its anatomy and variations. Eplasty. 2013 Jul 1;13:e35. PMID: 23882301; PMCID: PMC3701420. Pubmed