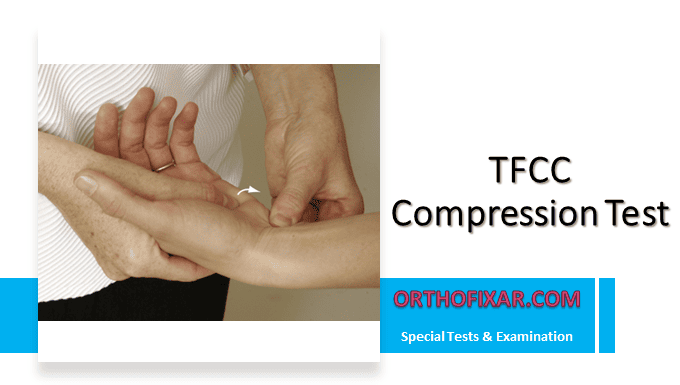
The TFCC Compression Test is a specialized examination technique used to evaluate potential pathology in the wrist’s triangular fibrocartilage complex.
The TFCC Compression Test becomes indicated when patients present with ulnar-sided wrist pain, particularly if there’s suspicion of distal ulnar head or styloid impingement on the lunate. Clinical signs suggesting potential TFCC pathology or considerations of ulnar impaction syndrome in the differential diagnosis also warrant this examination technique.
How to Perform the TFCC Compression Test?
The patient should be in a seated position with the affected arm accessible and the elbow flexed to 90 degrees to stabilize the forearm. The wrist is positioned in ulnar deviation to create the appropriate testing position.
The examiner stabilizes the forearm with one hand while maintaining the patient’s elbow at 90 degrees. Using the other hand, steady axial compression force is applied through the fourth and fifth metacarpals. The examiner maintains controlled pressure while observing the patient’s response and noting any pain or discomfort during the maneuver.

What is the Positive TFCC Compression Test?
A positive TFCC Compression Test is indicated by pain reproduction during the compression maneuver, typically manifesting as localized discomfort in the ulnar aspect of the wrist.
The positive test may indicate a central tear of the TFCC affecting the fibrocartilaginous disc, ulnar impaction syndrome where the ulnar head contacts the lunate and triquetrum, or degenerative TFCC changes particularly common in older patients.
When the TFCC Compression Test is positive, clinicians should consider various differential diagnoses including TFCC tears (both traumatic and degenerative), ulnar impaction syndrome, lunotriquetral ligament injury, extensor carpi ulnaris tendinopathy, and ulnar styloid fracture or nonunion.
The test has important limitations to consider. Results are not pathognomonic and require correlation with imaging and clinical history. The examination depends on patient cooperation and requires clear communication about expected sensations. Additionally, proper positioning and force application are crucial for examiner technique sensitivity.
Integration with Clinical Assessment
The TFCC Compression Test should be used alongside complementary examinations such as the TFCC Load Test, Ulnar Fovea Sign Test, Piano Key Test, and other provocative ulnar deviation maneuvers. Positive clinical findings should be correlated with appropriate imaging including MRI with or without contrast, wrist arthroscopy (considered the gold standard), and plain radiographs to assess bony anatomy.
References & More
- Young D, Papp S, Giachino A. Physical examination of the wrist. Hand Clin. 2010;26(1):21–36
- Dutton M. Orthopedic Examination, Evaluation and Intervention. New York: McGraw Hill; 2004.
- Prosser R, Harvey L, LaStayo P, et al. Provocative wrist tests and MRI are of limited diagnostic value for suspected wrist ligament injuries: a crosssectional study. J Physiother. 2011;57(4):247–253. PubMed
- Orthopedic Physical Assessment by David J. Magee, 7th Edition.