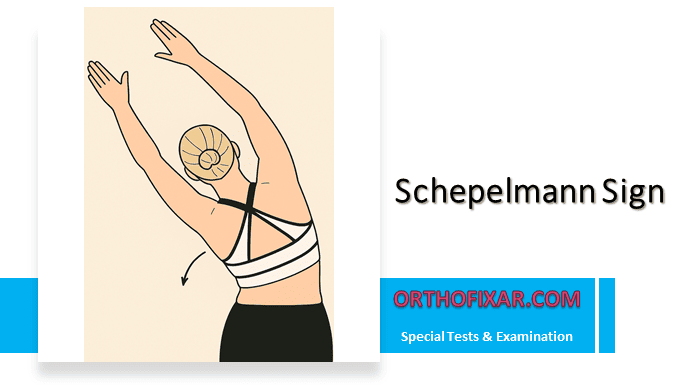
Schepelmann sign is a physical examination maneuver used to differentiate between musculoskeletal and pleuropulmonary causes of chest wall pain. Named after the physician who first described it, this test is particularly valuable when evaluating patients presenting with lateral thoracic pain.
How to Perform the Schepelmann Sign?
With the patient stands upright, both arms are elevated overhead. The patient performs lateral flexion (side bending) to one side. The maneuver is then repeated to the opposite side. The examiner notes the location and timing of any pain reproduction
See Also: Spine Examination

Clinical Interpretation
The diagnostic value of Schepelmann sign lies in understanding which side produces pain during the maneuver:
Pain on the Concave Side (Side of Bending)
When pain occurs on the concave side (the side toward which the patient is bending), this suggests:
- Intercostal muscle strain or inflammation – The muscles are being shortened and compressed
- Costovertebral joint pathology – Dysfunction at the articulation between the ribs and vertebral bodies
- Costotransverse joint pathology – Problems at the junction between the ribs and transverse processes of the vertebrae
The mechanism here is that lateral flexion causes compression of these structures on the concave side, reproducing pain if they are inflamed or injured.
Pain on the Convex Side (Side Away from Bending)
When pain occurs on the convex side (the side opposite to the direction of bending), this may indicate:
- Intercostal muscle strain – The muscles are being stretched, which can reproduce pain if they are injured
- Pleuropulmonary pathology – Conditions affecting the pleura or lungs, such as:
- Pleurisy (pleuritis)
- Pleural effusion
- Pneumonia with pleural involvement
- Non-organic lateral thoracic (NOLT) rib dysfunction – Mechanical rib dysfunctions that cause pain on stretching
The stretching of the intercostal spaces and expansion of the thoracic cavity on the convex side can aggravate pleural irritation or lung pathology.
See Also: Thoracic Spine Anatomy – A 12-Vertebrae Column
Clinical Significance of Schepelmann Sign
Differential Diagnosis Value:
- Helps distinguish between musculoskeletal and visceral causes of chest pain
- Assists in localizing the specific structures involved
- Guides further diagnostic workup and imaging decisions
Limitations:
- Not pathognomonic (specific) for any single condition
- Schepelmann Sign should be interpreted in context with:
- Patient history
- Other physical examination findings
- Additional diagnostic tests when indicated
Teaching Points for Medical Students
- Always correlate with history: Ask about trauma, recent respiratory infections, or chronic musculoskeletal conditions
- Perform bilaterally: Compare responses on both sides for asymmetry
- Observe carefully: Note not just presence of pain, but its quality, severity, and exact location
- Consider red flags: Severe pain, dyspnea, or systemic symptoms warrant urgent evaluation for serious pleuropulmonary disease
- Integration with other tests: Combine with chest wall palpation, respiratory examination, and percussion/auscultation.
Schepelmann sign is most useful in outpatient settings when evaluating:
- Chest wall pain of unclear etiology
- Suspected intercostal neuralgia
- Possible rib dysfunction or subluxation
- Differentiation of musculoskeletal from cardiac chest pain (in low-risk patients)
This simple bedside maneuver, requiring no equipment, exemplifies the enduring value of thorough physical examination skills in modern clinical practice.
References & More
- Fazekas D, Doroshenko M, Horn DB. Intercostal Neuralgia. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: PubMed
- Evans RC. Illustrated Orthopedic Physical Assessment. 3rd ed. St Louis: Elsevier; 2009.
- Orthopedic Physical Assessment by David J. Magee, 7th Edition.