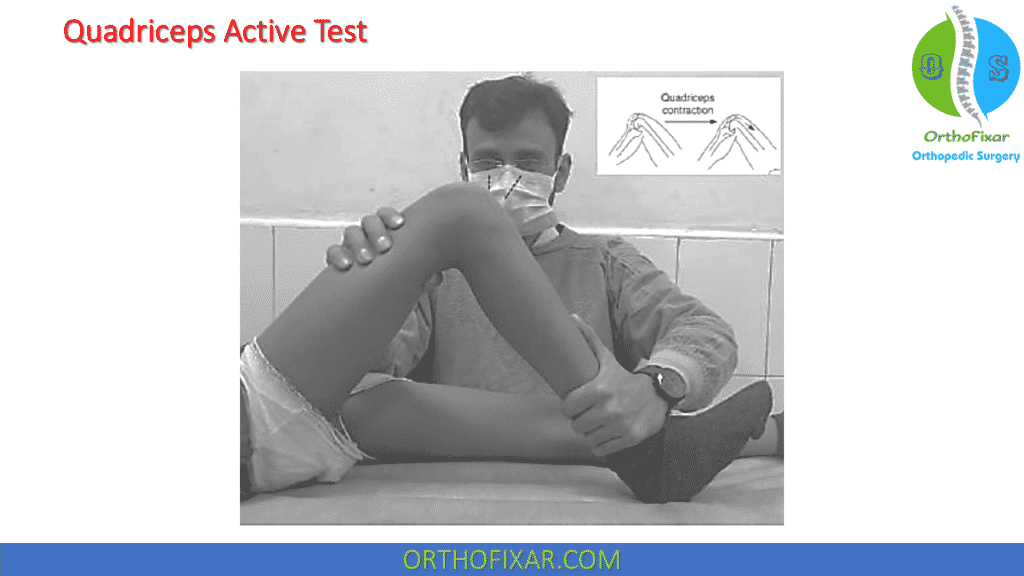
Quadriceps Active Test (also called the Active Drawer Test) is used to evaluate the posterior cruciate ligament injury at the knee joint. This test works by contractions of the quadriceps being transmitted to the tibial tubercle via the patella and the patellar tendon.
The Quadriceps Active Test can also be used to evaluate the anterior cruciate ligament injury, but it is a better expression of posterior cruciate insufficiency than of anterior cruciate insufficiency.
How do you perform the Quadriceps Active Test?
- The patient lies in the supine position.
- The relaxed limb is supported with the knee flexed to 90 degrees in the drawer test position, hip is flexed 45° and the foot is in neutral position.
- The patient is asked to execute a gentle quadriceps contraction to shift the tibia without extending the knee.
- Another way to perform the test is by fixing the foot and asking the patient to try to extend the leg. If there is a posterior sag the quadriceps will pull the tibia forwards.
- Muller advocated allowing the foot to be free and noting when the foot is lifted off the table, which occurs only after the tibia has shifted forward and stabilized.
See Also:
- Posterior cruciate ligament injury
- Posterior Drawer Test of the Knee
- Posterior Sag Sign
- Knee Ligaments Anatomy
What does a positive Quadriceps Active Test mean?
If the PCL is ruptured, the tibia sags into posterior subluxation (2 mm or more), and the patellar ligament is then directed anteriorly. Contraction of the quadriceps causes the tibia to shift forward to its normal position, indicating a positive test for a torn posterior cruciate ligament.
If there is no posterior sag present and if the tibia shifts forward more on the injured side than the noninjured side, it is a positive test for anterior cruciate ligament disruption

Test Reliability
Studies have shown significantly different sensitivities for this test.
Rubinstein et al. reported a sensitivity and a specificity of:
- Sensitivity: 54%
- Specificity: 97%
He found that the posterior drawer test, which included palpation of the tibia-femur step-off, was the most sensitive and specific clinical test for PCL injury.
Another study by Daniel reported a sensitivity of 98% for detecting the PCL injury.
Notes
In a normal knee, flexed 90°, the patellar tendon lies posteriorly oriented and active pull of the quadriceps does not result in an anterior shift of the tibia. In a PCL deficient knee, there is posterior subluxation of the tibia over the distal femur in a flexed knee position. The patellar tendon in such situations is directed more anteriorly, and active quadriceps contraction will result in anterior shift of the tibia.
Interpretation of the results of this test is more accurate in the presence of higher-grade or chronic PCL lesions.
References
- Daniel DM, Stone ML, Barnett P, Sachs R. Use of the quadriceps active test to diagnose posterior cruciate-ligament disruption and measure posterior laxity of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988 Mar;70(3):386-91. PMID: 3346263. PubMed
- Rubinstein RA Jr, Shelbourne KD, McCarroll JR, VanMeter CD, Rettig AC. The accuracy of the clinical examination in the setting of posterior cruciate ligament injuries. Am J Sports Med. 1994 Jul-Aug;22(4):550-7. doi: 10.1177/036354659402200419. PMID: 7943523. PubMed
- Daniel DM, Stone ML, Barnett P, et al: Use of the quadriceps active test to diagnose posterior cruciate-ligament disruption and measure posterior laxity of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am 70:386–391, 1988.
- De Lee JC. Ligamentous injury of the knee. In: Stanitski CL, DeLee JC, Drez D, eds. Pediatric and Adolescent Sports Medicine. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1994.
- Muller W. The Knee: Form, Function and Ligament Reconstruction. New York: Springer-Verlag; 1983.
- Dutton’s Orthopaedic Examination, Evaluation, And Intervention 3rd Edition.