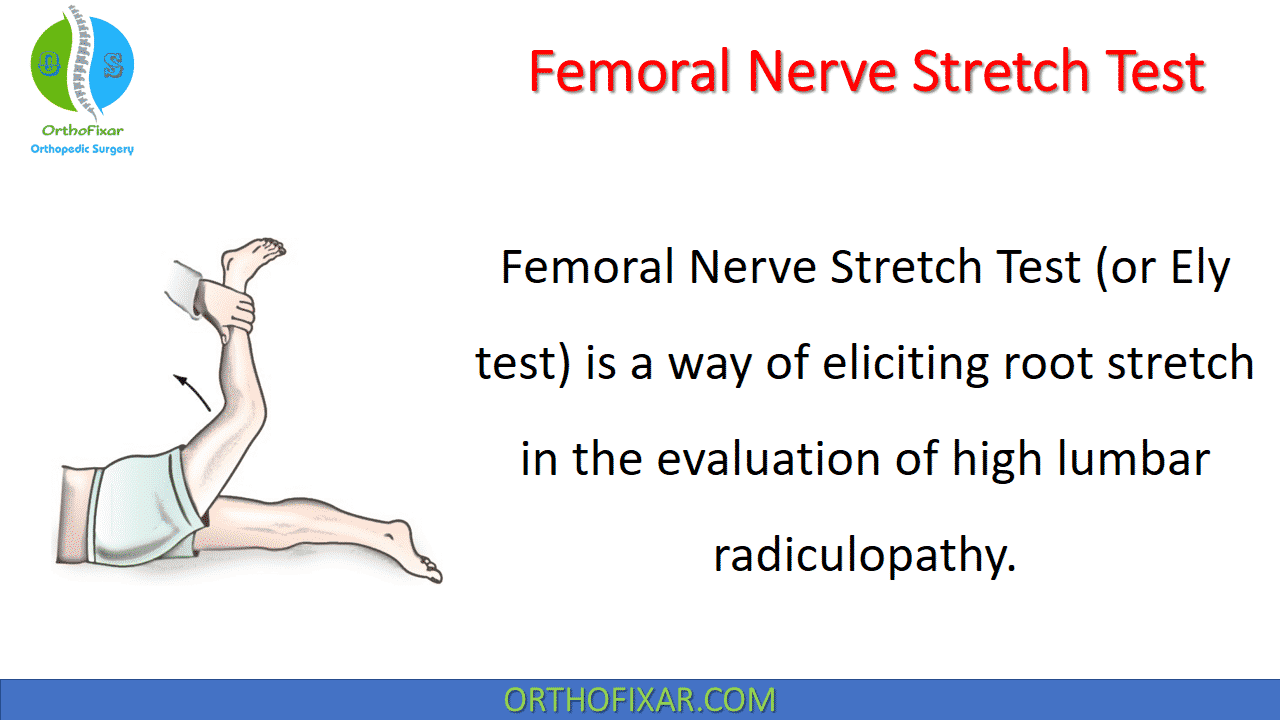
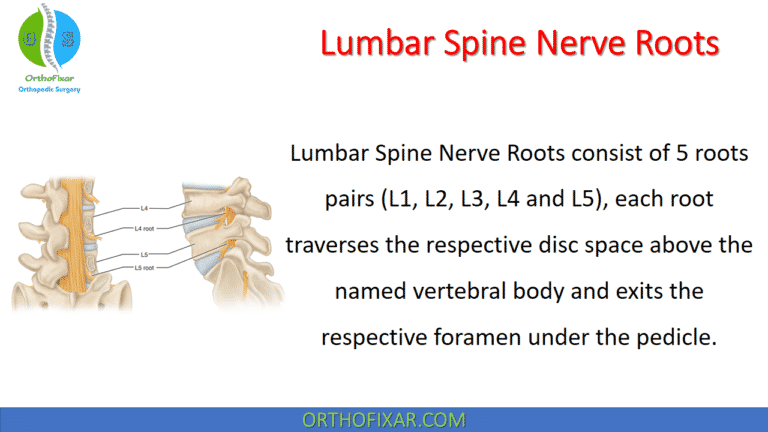
The Femoral Nerve Stretch Test is used to assess irritation of the upper lumbar nerve roots (L2-L3–L4) and the femoral nerve. It’s useful when evaluating patients with suspected lumbar radiculopathy, anterior thigh pain, or high lumbar disc pathology.
As noted, the straight leg raising test and its variants do not place significant tension on the nerve roots above L5. Although compression of the upper lumbar nerve roots is not common, it does occur. Herniations of the L3–L4 disc commonly compress the L4 nerve root.
How do you perform the Femoral Nerve Stretch Test?
To perform the femoral nerve stretch test:
- The patient lies prone on the examination table with a pillow under the abdomen,
- the knee is pulled into maximum flexion, or the examiner pulls upward on the extended knee to passively extend the hip.
- In the bent knee pulling test, the patient’s knee is flexed and the examiner pulls upward on the ankle while pushing the buttock forward (in the same way as for eliciting the psoas sign used in the diagnosis of appendicitis).
See Also: Lasegue Test
The femoral stretch test can be done with side-lying position:
- The patient lies on the unaffected side with the unaffected limb flexed slightly at the hip and knee
- The patient’s back should be straight, not hyperextended. The patient’s head should be slightly flexed.
- The examiner grasps the patient’s affected or painful limb and extends the knee while gently extending the hip approximately 15°.
- The patient’s knee is then flexed on the affected side; this movement further stretches the femoral nerve.
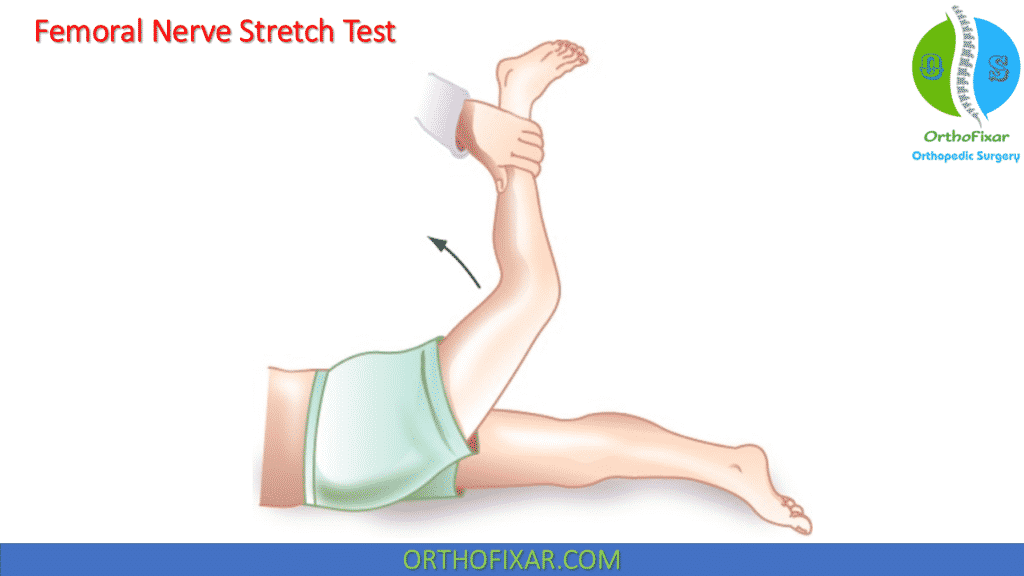
What does a positive Femoral Nerve Stretch Test mean?
In the normal patient, this maneuver induces only a mild feeling of tightness in the anterior thigh. When one of the nerve roots that contribute to the femoral nerve is compressed, this maneuver reproduces the patient’s radicular pain in the anterior thigh (positive Femoral Nerve Stretch Test).
This test is associated with a high number of false positives due to tight or injured quadriceps. The cross femoral stretch is positive when testing the opposite leg produces symptoms on the involved side.
Accuracy
The femoral nerve stretch test has been shown to be positive in 84–95% of patients with high lumbar disks, although the test may be falsely positive in the presence of an adaptively shortened iliopsoas or rectus femoris or any pathology in or about the hip joint, sacroiliac joint, and lumbar spine.
Differential Diagnosis
A positive Femoral Nerve Stretch Test may indicate:
- Lumbar disc herniation (L2–L4)
- Lumbar spinal stenosis
- Psoas abscess
- Retroperitoneal mass
- Diabetic femoral neuropathy
Correlation with imaging (MRI) and neurological examination is recommended for definitive diagnosis.
Notes
The femoral nerve stretch test is probably the single best screening test to evaluate for a high lumbar radiculopathy.
This is also a traction test for the nerve roots at the mid-lumbar area (L2–L4). As with the straight leg raising test, there is also a contralateral positive test. That is, when the test is performed, the symptoms occur in the opposite limb. This is called the crossed femoral stretching test. Pain in the groin and hip that radiates along the anterior medial thigh indicates an L3 nerve root problem; pain extending to the mid-tibia indicates an L4 nerve root problem.
The femoral nerve stretch test is similar to Ober’s test for a tight iliotibial band, so the examiner must be able to differentiate between the two conditions. If the iliotibial band is tight, the test leg does not adduct but remains elevated away from the table as the tight tendon riding over the greater trochanter keeps the leg abducted. Femoral nerve injury presents with a different history, and the referred pain (anteriorly) tends to be stronger.
Femoral Nerve Stretch Test vs. Straight Leg Raise Test
| Feature | Femoral Nerve Stretch Test | Straight Leg Raise |
|---|---|---|
| Assesses | L2–L4 | L4–S1 |
| Pain location | Anterior thigh | Posterior thigh & leg |
| Patient position | Prone | Supine |
Femoral Nerve Anatomy
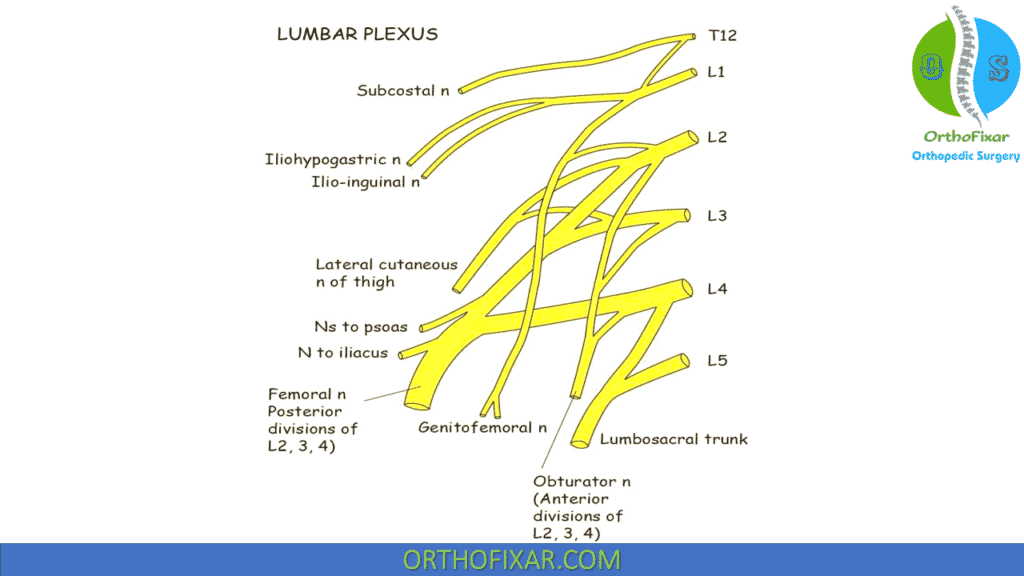
The femoral nerve, the largest branch of the lumbar plexus (L2-L4), arises from the lateral border of the psoas just above the inguinal ligament. The nerve descends beneath this ligament to enter the femoral triangle on the lateral side of the femoral artery, where it divides into terminal branches.
Above the inguinal ligament, the femoral nerve supplies the iliopsoas muscle, and, in the thigh, it supplies the sartorius, pectineus, and quadriceps femoris muscles.
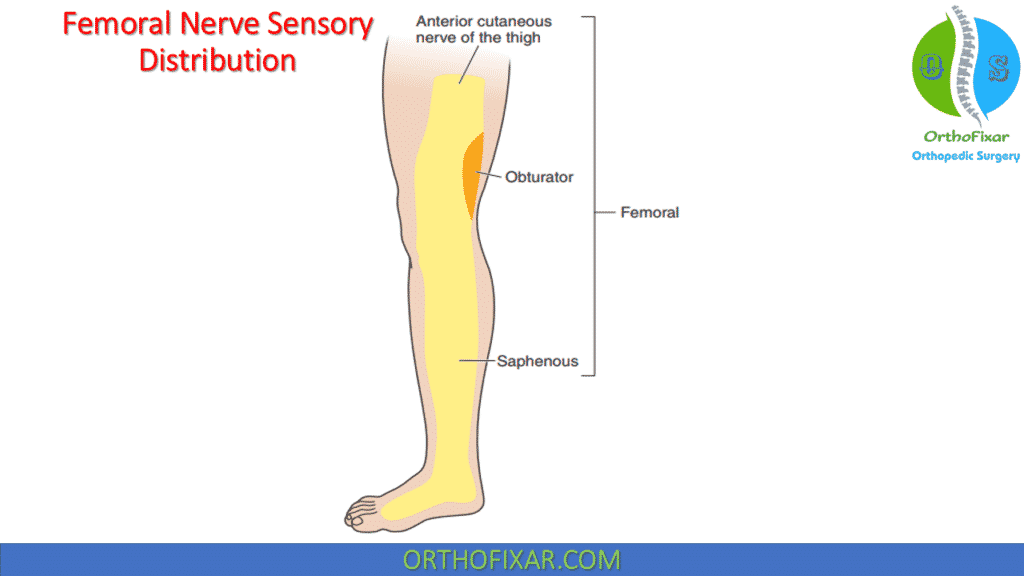
The sensory distribution of the femoral nerve includes the anterior and medial surfaces of the thigh via the anterior femoral cutaneous nerve and the medial aspect of the knee, the proximal leg, and articular branches to the knee via the saphenous nerve, the largest cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve.
The saphenous nerve exits from the adductor (Hunter’s, or subsartorial) canal, descends under the sartorius muscle, and then winds around the posterior edge of the sartorius muscle at its tendon portion.
References
- Nadler SF, Malanga GA, Stitik TP, Keswani R, Foye PM. The crossed femoral nerve stretch test to improve diagnostic sensitivity for the high lumbar radiculopathy: 2 case reports. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001 Apr;82(4):522-3. doi: 10.1053/apmr.2001.22343. PMID: 11295015. PubMed
- Dyck P. The femoral nerve traction test with lumbar disc protrusion. Surg Neurol. 1976;6:163–166. PubMed
- Sarvdeep S. Dhatt, Sharad Prabhakar – Handbook of Clinical Examination in Orthopedics. An Illustrated Guide-Springer Singapore.
- Dutton’s Orthopaedic Examination, Evaluation, And Intervention 3rd Edition.
- AG, Swenson RS. Disorders of the Nervous System: A Primer. New Haven: Dartmouth Medical School, 2004. Retrieved on August 28, 2018.
- Kreitz BG, Coté P, Yong-Hing K. Crossed femoral stretching test: a case report. Spine I. 1996;21:1584–1586. PubMed