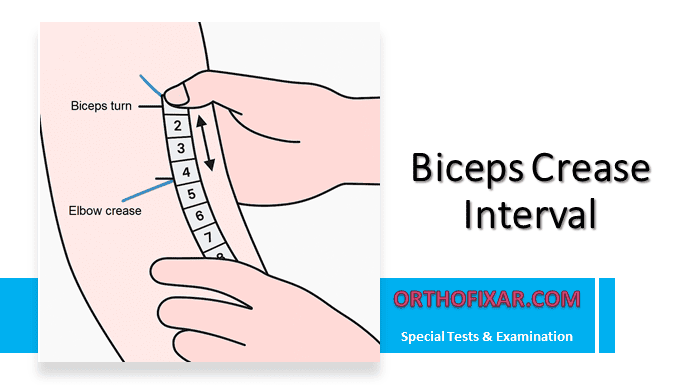
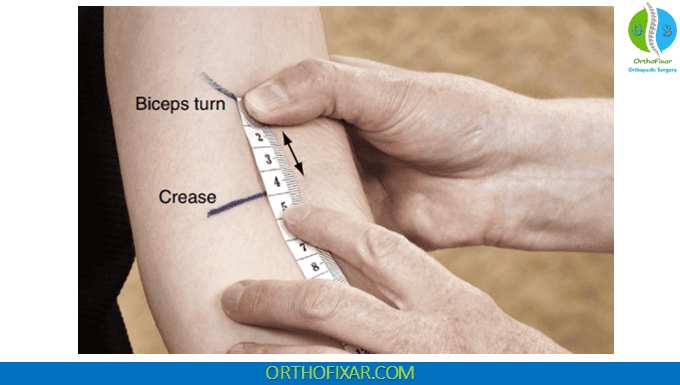
The Biceps Crease Interval (BCI) is a clinical measurement technique used to diagnose distal biceps tendon ruptures at the elbow joint. This physical examination method provides clinicians with an objective measurement that can help differentiate between intact and ruptured distal biceps tendons, particularly when clinical presentation may be ambiguous.
Anatomy Overview
The distal biceps tendon inserts on the radial tuberosity of the radius bone. When this tendon ruptures, the biceps muscle belly retracts proximally, creating an increased distance between the muscle belly and the antecubital fossa (elbow crease). The Biceps Crease Interval measures the distance between the distal aspect of the biceps muscle and the flexion crease of the elbow.
See Also: Distal Biceps Tendon Tear
How to measure the Biceps Crease Interval?
The patient should be seated comfortably with both arms accessible for examination. It is good to begin the assessment with the unaffected arm to establish a baseline measurement and familiarize yourself with the palpation technique.
- Initial Positioning: Start with the patient’s unaffected arm in flexion, then fully extend the elbow to create tension in the biceps muscle and clearly define anatomical landmarks.
- Establish the Proximal Landmark: Draw a line across the flexion crease in the antecubital fossa. This serves as your fixed reference point and represents the anatomical boundary of the elbow joint.
- Identify the Distal Biceps Border: Using light palpation, stroke the contour of the distal biceps muscle back and forth along its central longitudinal axis. The goal is to identify the precise point where the distal biceps begins its sharpest turn toward the antecubital fossa. This requires careful palpation to distinguish muscle belly from tendinous tissue.
- Mark the Distal Cusp: Once identified, mark a transverse line at the distal cusp of the biceps muscle belly. This represents the most distal extent of the palpable muscle tissue.
- Measurement: Measure the perpendicular distance between the two transverse lines using a ruler or measuring tape. Record this measurement as the BCI.
- Bilateral Comparison: Repeat the identical process on the contralateral arm to allow for comparison.
Biceps Crease Interval Normal Values
- Normal BCI: 4.8 cm ± 0.6 cm for both dominant and non-dominant arms
- Normal range: Approximately 4.2-5.4 cm
Positive Test Criteria
The test is considered positive for distal biceps tendon rupture when either of the following conditions is met:
- Absolute Measurement: Biceps Crease Interval greater than 6.0 cm
- Relative Measurement: Biceps crease ratio greater than 1.2
Biceps Crease Ratio Calculation
The biceps crease ratio compares the injured arm to the uninjured arm: Biceps Crease Ratio = BCI (injured arm) / BCI (uninjured arm)
A ratio exceeding 1.2 suggests significant retraction of the biceps muscle belly, indicating likely tendon rupture.
Clinical Significance
The Biceps Crease Interval test addresses a common clinical challenge in diagnosing distal biceps tendon ruptures. While complete ruptures may present with obvious deformity and loss of function, partial tears or chronic injuries can be more subtle. The objective nature of this measurement helps clinicians make more confident diagnostic decisions.
Advantages of the BCI Test
- Objective measurement rather than subjective assessment
- Non-invasive and requires no special equipment
- Quick to perform in clinical settings
- Bilateral comparison accounts for individual anatomical variation
- Standardized technique allows for consistent application across different examiners
Limitations and Considerations
While the Biceps Crease Interval is a valuable diagnostic tool, clinicians should be aware of its limitations. Factors such as patient body habitus, muscle development, and examiner experience can influence measurement accuracy. Additionally, the test should be used in conjunction with other clinical findings, patient history, and imaging studies when indicated.
Integration with Clinical Practice
The Biceps Crease Interval measurement should be incorporated into a comprehensive physical examination that includes assessment of strength, range of motion, and other provocative tests such as the hook test or biceps squeeze test. When combined with appropriate imaging studies, the Biceps Crease Interval can significantly enhance diagnostic accuracy for distal biceps tendon injuries.
References & More
- Zwerus EL, Somford MP, Maissan F, et al. Physical examination of the elbow, what is the evidence? A systematic literature review. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51:1–9. Pubmed
- Devereaux MW, ElMaraghy AW. Improving the rapid and reliable diagnosis of complete distal biceps tendon rupture: a nuanced approach to the clinical examination.Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(9):1998–2004. Pubmed
- ElMaraghy A, Devereaux M, Tsoi K. The biceps crease interval for diagnosing complete distal biceps tendon ruptures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466:2255–2262. Pubmed
- Orthopedic Physical Assessment by David J. Magee, 7th Edition.