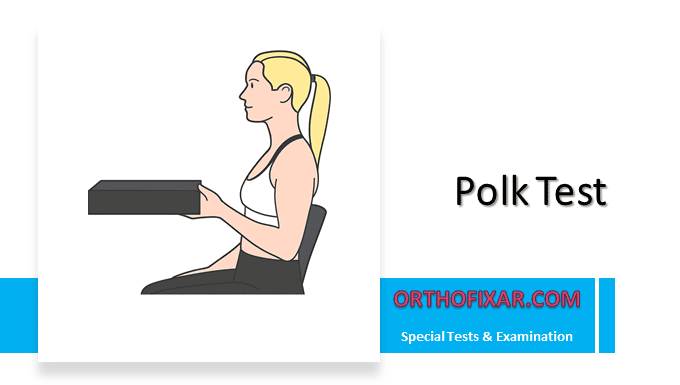
Polk Test is used to differentiate between lateral and medial epicondylitis (commonly known as tennis elbow and golfer’s elbow, respectively). This weight-bearing test helps clinicians identify the specific location and nature of elbow pain through controlled loading of the affected structures.
How to perform the Polk Test?
The patient is positioned in a seated position with the elbow flexed to approximately 90 degrees.
Polk Test consists of two distinct phases, each designed to stress different anatomical structures around the elbow:
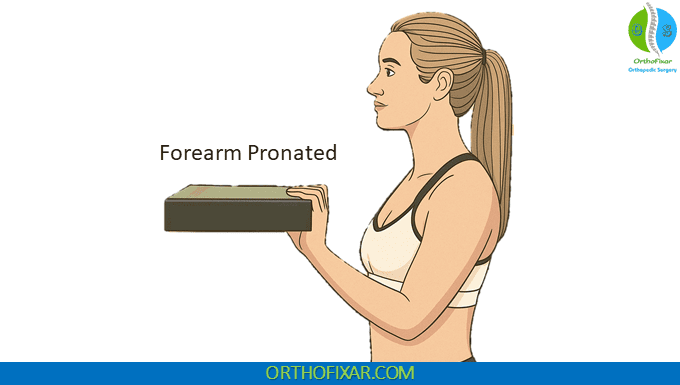
Phase 1: Pronated Forearm Position The patient begins with the forearm in a pronated position (palm facing downward). While maintaining this position, the patient is instructed to lift the 2.5-kg weight by flexing the elbow. During this motion, the examiner observes for pain localization and assesses the patient’s ability to complete the movement.
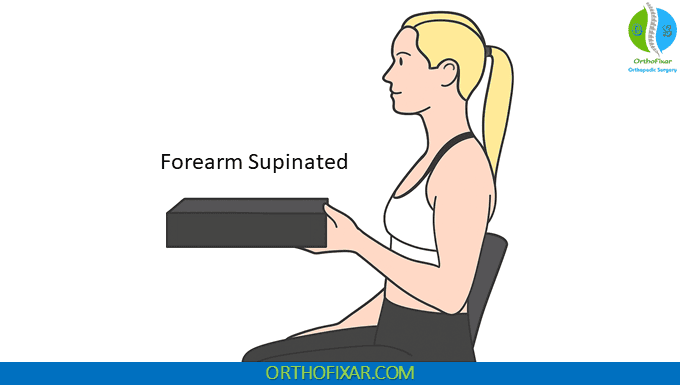
Phase 2: Supinated Forearm Position The patient then repeats the identical lifting motion with the forearm supinated (palm facing upward). Again, the examiner monitors for pain location and movement quality.
What is the result of the Polk Test?
Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow)
When pain occurs in the lateral epicondyle region during the pronated lifting phase, this suggests lateral epicondylitis. The pronated position places increased stress on the extensor muscles that originate from the lateral epicondyle, particularly the extensor carpi radialis brevis, which is commonly involved in lateral epicondylitis.
See Also: Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow)
Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer’s Elbow)
Pain localized to the medial epicondyle during the supinated lifting phase indicates possible medial epicondylitis. The supinated position with elbow flexion increases the load on the flexor-pronator muscle group that originates from the medial epicondyle.
See Also: Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer's Elbow)
References & More
- Polkinghorn BS. A novel method for assessing elbow pain resulting from epicondylitis. J Chiropr Med. 2002;1(3):117–121. Pubmed
- Zwerus EL, Somford MP, Maissan F, et al. Physical examination of the elbow, what is the evidence? A systematic literature review. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51:1–9. Pubmed
- Orthopedic Physical Assessment by David J. Magee, 7th Edition.