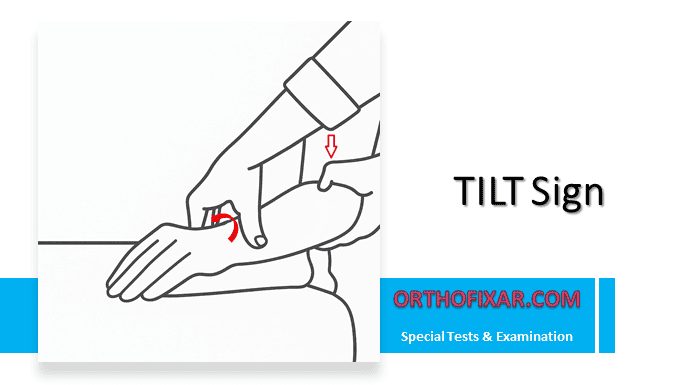
The TILT sign represents a valuable clinical examination technique for detecting partial tears of the distal biceps tendon. This physical examination maneuver provides clinicians with a reliable method to assess the integrity of the biceps insertion at the radial tuberosity, particularly when complete rupture is not evident but clinical suspicion remains high.
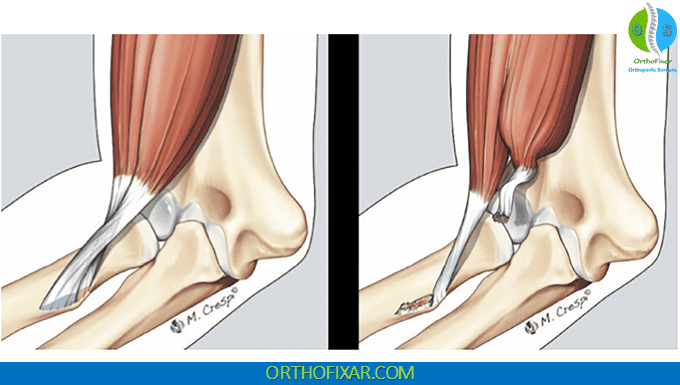
The biceps brachii muscle terminates as a tendon that inserts primarily onto the radial tuberosity, located on the medial aspect of the proximal radius. This insertion point sits approximately 2.5 cm (1 inch) distal to the radial head.
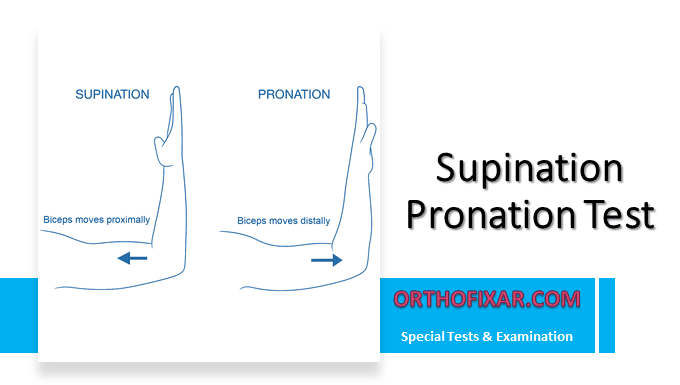
The radial tuberosity’s position changes dramatically with forearm rotation. During supination, the tuberosity rotates medially and becomes largely inaccessible to palpation due to overlying soft tissues and muscle bulk. While during full pronation, the tuberosity rotates laterally, bringing it into a position where it can be directly palpated through the skin.
See Also: Distal Biceps Tendon Tear
How is TILT Sign Performed?
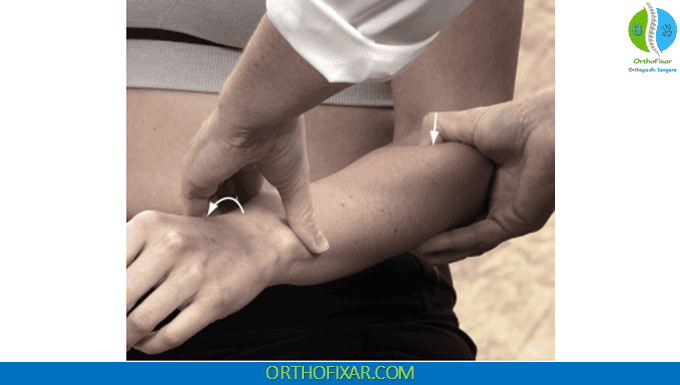
The patient is seated with the elbow flexed to 90°:
- First, locate the radial head through palpation. The radial tuberosity lies approximately 2.5 cm distal to this landmark.
- Place firm pressure over the anticipated location of the radial tuberosity while systematically moving the forearm through supination and pronation.
- The key to successful examination lies in achieving full pronation. Only in this position does the radial tuberosity rotate sufficiently lateral to become palpable through the overlying tissues.
- Apply consistent, firm pressure while the arm moves through its range of motion, paying particular attention to any tenderness that emerges specifically during full pronation.
What does a Positive TILT Sign Mean?
A positive test manifests as tenderness over the lateral (radial) aspect of the tuberosity that becomes apparent only when the forearm reaches full pronation. This specific pattern—tenderness localized to the insertion site and position-dependent presentation—suggests partial disruption of the distal biceps tendon fibers.
The TILT sign’s diagnostic value lies in its ability to detect partial tears that might otherwise be missed. Unlike complete ruptures, which present with obvious deformity and loss of function, partial tears can be subtle and easily overlooked without systematic examination.
A Case Report found this TILT sign diagnostic test to be 100% sensitive for diagnosing partial distal biceps brachii tendon tears.
Differential Considerations
When interpreting the TILT sign, consider alternative sources of lateral elbow pain:
- Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow)
- Radial tunnel syndrome
- Posterior interosseous nerve entrapment
- Radiocapitellar joint pathology
The position-specific nature of TILT sign tenderness helps differentiate biceps pathology from these other conditions, which typically present with different pain patterns and provocative maneuvers.
Clinical Correlation
A positive TILT sign should prompt further evaluation including:
- Detailed history focusing on mechanism of injury
- Assessment of biceps strength and endurance
- Evaluation of supination power
- Consideration of advanced imaging (MRI) for definitive diagnosis
Limitations and Considerations
While the TILT sign provides valuable clinical information, several factors can influence its reliability:
- Patient body habitus may affect palpation accuracy
- Acute swelling can obscure anatomical landmarks
- Patient guarding or anxiety may create false positives
- Examiner experience significantly impacts test sensitivity
References & More
- Shim SS, Strauch RJ. A novel clinical test for partial tears of the distal biceps brachii tendon: the TILT sign. Clin Anat. 2018;31(2):301–303. Pubmed
- Orthopedic Physical Assessment by David J. Magee, 7th Edition.