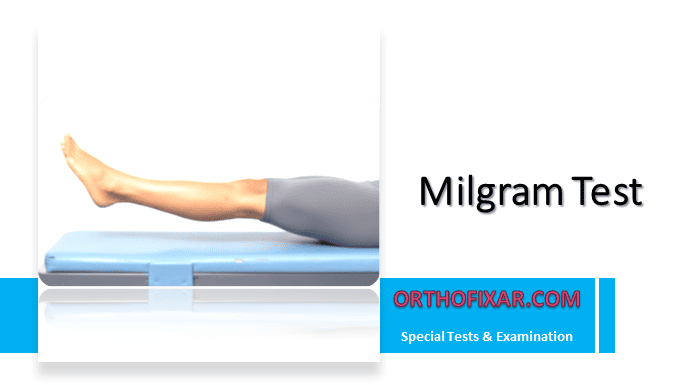
The Milgram Test is a clinical examination procedure used to assess for lumbar spine pathology, particularly space-occupying lesions such as herniated discs, intrathecal pressure increases, or other causes of nerve root compression.
This test evaluates the ability of the patient to maintain lower limb elevation under stress, indirectly assessing lumbar spine stability, intrathecal pressure, and potential nerve root irritation.
How to Perform the Milgram Test of the Spine?
- The patient lies supine on the examination table.
- The patient is instructed to raise both legs simultaneously approximately 5–10 cm (2–4 inches) off the table.
- The legs should be kept straight (knees extended).
- The patient attempts to hold this position for 30 seconds.
See Also: Lumbar Spine Nerve Roots

What does a Positive Milgram Test Mean?
The test is considered positive if:
- The patient is unable to maintain the leg position for 30 seconds, or
- The maneuver reproduces pain, tingling, or other symptoms in one or both lower limbs.
A positive result may indicate pressure on nerve roots due to intervertebral disc protrusion or space-occupying lesions within the spinal canal that compromise the cauda equina or lumbosacral nerve roots.
Because this test places significant stress on the lumbar spine, it should be performed with caution, especially in patients with known or suspected disc pathology or acute low back pain. Failure to hold the position may also reflect core muscle weakness or instability of the lumbar spine.
Summary
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Test Name | Milgram Test |
| Patient Position | Supine |
| Examiner Instruction | Lift both legs 5–10 cm off table and hold for 30 seconds |
| Positive Finding | Pain or inability to hold legs up |
| Indicates | Lumbar disc pathology, space-occupying lesion, nerve root irritation |
| Precaution | High load on lumbar spine—use caution |
References & More
- Palmer ML, Epler M. Clinical Assessment Procedures In Physical Therapy. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 1990.
- Orthopedic Physical Assessment by David J. Magee, 7th Edition.
- ResearchGate