Sternoclavicular joint pain and swelling can be alarming, especially when symptoms persist or worsen over time. The sternoclavicular (SC) joint connects the collarbone (clavicle) to the breastbone (sternum) and plays a vital role in shoulder movement and upper limb stability. While most causes of SC joint pain and swelling are benign, many people worry whether sternoclavicular joint swelling could be related to cancer symptoms.
Understanding the possible causes, warning signs, and when to seek medical evaluation is essential for early diagnosis and peace of mind.
What is Sternoclavicular Joint Pain and Swelling?
Sternoclavicular joint pain occurs when there is injury or dysfunction within the SC joint. This pain can arise from various conditions, including trauma, arthritis, or inflammatory disorders. Because the SC joint is essential for shoulder movement, any issues in this area can cause pain when lifting the arm, moving the shoulder, or even during deep breathing.
Although sternoclavicular joint swelling is rarely caused by cancer, persistent or unexplained swelling should always be properly evaluated.
Learn About Sternoclavicular Joint Anatomy

Common Causes of SC Joint Pain
Trauma or Injury: Direct impact to the joint, such as from a fall, car accident, or sports injury, can cause dislocation or sprain of the SC joint, leading to acute pain.
Arthritis: Both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can affect the SC joint. Osteoarthritis causes the breakdown of cartilage, while rheumatoid arthritis results from inflammation in the joint, both leading to chronic pain and stiffness.
Infections: Though rare, infections in the SC joint can occur and cause pain, swelling, and redness. Prompt medical attention is necessary if an infection is suspected.
Inflammation: Conditions like costochondritis, which cause inflammation in the rib area, may also affect the SC joint and cause localized pain.
Sternoclavicular Joint Swelling and Cancer Symptoms
In rare cases, sternoclavicular joint swelling may be associated with cancer, either due to:
- Bone tumors (primary or metastatic)
- Lymphoma
- Metastatic cancers from the lung, breast, or head and neck region
Warning Signs That May Suggest Cancer-Related SC Joint Swelling
Seek medical evaluation if sternoclavicular joint swelling is accompanied by:
- Painless, progressive swelling
- Night pain or pain at rest
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Persistent swelling despite treatment
- Hard or fixed mass over the joint
- History of cancer
While these symptoms do not automatically indicate cancer, they warrant further investigation such as imaging and laboratory tests.
Symptoms of SC Joint Pain
Localized pain: The pain is typically felt at the junction of the collarbone and sternum, especially during shoulder movement.
Swelling or tenderness: The area around the joint may become swollen or sensitive to touch.
Limited range of motion: Individuals may find it difficult to raise their arms or perform overhead movements.
Clicking or popping sounds: Some may experience clicking or popping noises when moving the shoulder, indicating joint instability or dislocation.
Visible deformity: In more severe cases, such as dislocations, the joint may appear visibly misaligned.
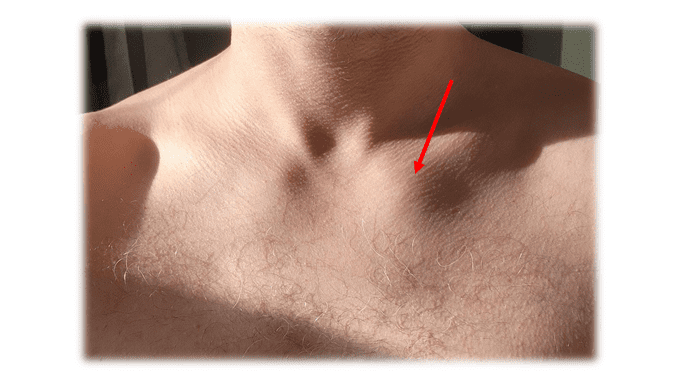
Diagnosis of Sternoclavicular Joint Swelling & Pain
To rule out serious causes, including cancer, doctors may order:
- X-ray to assess joint alignment and bone changes
- CT scan for detailed bone evaluation
- MRI to assess soft tissues, inflammation, or tumors
- Blood tests if infection or inflammatory disease is suspected
- Biopsy (only if imaging raises concern for malignancy)
SC Joint Pain Treatment Options
Treatment for sternoclavicular joint pain depends on the underlying cause and severity. The goal is to reduce pain, restore function, and prevent further injury.
Rest and Activity Modification: Reducing activities that aggravate the SC joint is often the first step in managing pain. Rest allows the joint to heal, particularly in cases of sprains or minor injuries.
Medications:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Corticosteroid Injections: For more severe pain or chronic inflammation, corticosteroid injections directly into the SC joint can provide relief.
Physical Therapy: A tailored rehabilitation program can help improve joint stability, increase range of motion, and strengthen surrounding muscles. Physical therapists focus on exercises that enhance shoulder and chest mobility without placing strain on the SC joint.
Ice and Heat Therapy: Applying ice to the affected area can reduce swelling, especially in the initial stages of injury. Heat therapy, on the other hand, can help relax tight muscles and improve blood circulation, promoting healing.
Bracing or Sling: In cases of SC joint dislocation or severe instability, wearing a brace or sling may be necessary to immobilize the joint and allow it to heal.
Surgical Intervention: Surgery is generally considered a last resort for SC joint pain treatment. In cases of persistent pain, chronic dislocations, or severe joint degeneration, surgical repair or reconstruction may be required. Procedures range from repairing the damaged ligaments to removing part of the clavicle.

When to See a doctor?
You should seek medical attention if you experience:
- Persistent sternoclavicular joint swelling
- Rapidly enlarging mass
- Fever or signs of infection
- Difficulty breathing
- Night pain or unexplained weight loss
- History of cancer with new SC joint symptoms
Early diagnosis significantly improves outcomes and rules out serious conditions.
Conclusion
Sternoclavicular joint pain can be uncomfortable, but with the right treatment approach, most people can manage their symptoms effectively. Whether the cause is trauma, arthritis, or inflammation, there are various Sternoclavicular joint pain treatments available to reduce discomfort and improve quality of life. If you are experiencing persistent SC joint pain, consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment planning.
References & More
- Orthoinfo – AAOS
- Kiel J, Ponnarasu S, Kaiser K. Sternoclavicular Joint Injury. [Updated 2023 Aug 28]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: Pubmed
- Sharma D, Dhiman P, Menon J, Krishna KV. Sternocostoclavicular Joint Swelling; Diagnosis of a Neglected Entity. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2015 Apr;3(2):94-8. PMID: 26110174; PMCID: PMC4468627. Pubmed
- Edwin J, Ahmed S, Verma S, Tytherleigh-Strong G, Karuppaiah K, Sinha J. Swellings of the sternoclavicular joint: review of traumatic and non-traumatic pathologies. EFORT Open Rev. 2018 Aug 25;3(8):471-484. doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.3.170078. PMID: 30237905; PMCID: PMC6134883. Pubmed