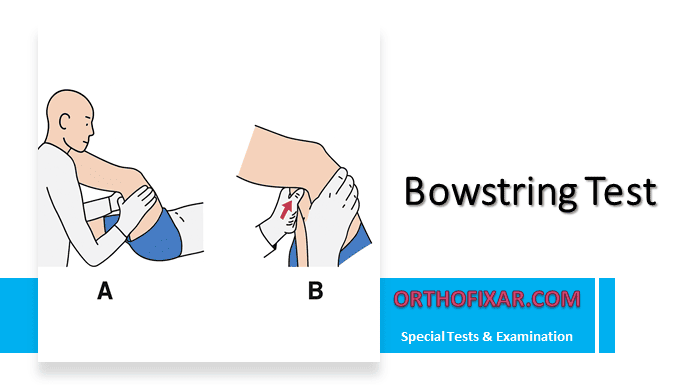
The Bowstring Test is a clinical maneuver used to assess sciatic nerve tension or irritation, often performed as a modification of the Straight Leg Raising (SLR) Test. It helps in detecting nerve root compression, typically associated with lumbar disc herniation. It’s sometimes called the Cram Test or Popliteal Pressure Sign.
The sciatic nerve is the largest nerve in the human body, originating from the L4-S3 nerve roots. It exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen and courses down the posterior thigh, passing through the popliteal fossa before dividing into the tibial and common peroneal nerves. During the straight leg raising maneuver, the sciatic nerve is stretched and tensioned. Any pathology causing nerve root compression (such as a herniated disc) or nerve inflammation will produce pain when this tension is applied. The Bowstring Test exploits this principle by adding localized pressure to the nerve at the popliteal fossa.
See Also: Sciatic Nerve Anatomy
How to Perform the Bowstring Test?
Supine Version
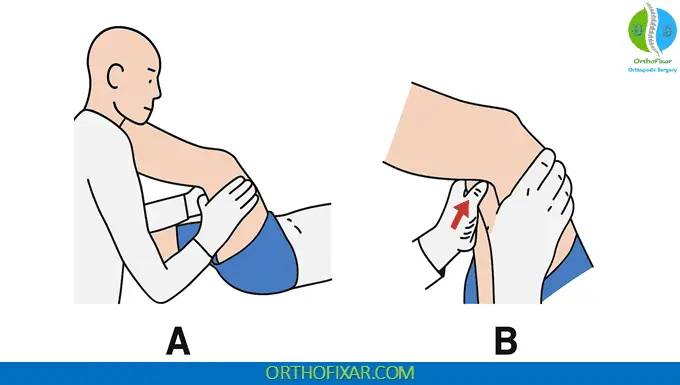
- The examiner performs a Straight Leg Raise (SLR) on the affected side until the patient reports pain or radicular symptoms radiating down the leg (Fig. 9.51).
- Without changing the position of the thigh, the examiner slightly flexes the knee—about 20 degrees—which usually reduces the symptoms.
- The examiner then applies firm pressure with the thumb or fingers over the popliteal fossa (where the sciatic nerve runs).
- Reproduction of the patient’s pain or paresthesia constitutes a positive Bowstring Test.
Seated Position (Sciatic Tension Test/Deyerle’s Sign)
- The patient sits on the edge of the examination table with knees flexed. The examiner passively extends the patient’s knee, producing pain through sciatic nerve tension.
- The examiner slightly flexes the knee until the pain and radicular symptoms disappear. The examiner maintains this position by clasping the patient’s leg between their own knees, stabilizing the limb.
- With the leg stabilized, the examiner presses the fingers of both hands deeply into the popliteal space. Pain resulting from this maneuver indicates a positive test.
See Also: Lasegue Test | Straight Leg Raise Test
What is the Positive Bowstring Test?
Reproduction of the patient’s pain or paresthesia constitutes a positive Bowstring Test.
A positive Bowstring Test indicates tension or pressure on the sciatic nerve. The localized pressure in the popliteal fossa reproduces the radicular symptoms that were present during the initial straight leg raise but had been relieved by knee flexion.
This finding suggests:
- Nerve root compression (commonly from disc herniation at L4-L5 or L5-S1 levels) .
- Sciatic nerve irritation or inflammation .
- True radiculopathy rather than muscular or non-neurogenic pain.
If popliteal pressure does not reproduce the radicular symptoms, the test is negative. This may suggest:
- The initial pain during SLR was muscular (hamstring tightness) rather than neurogenic,
- No significant sciatic nerve pathology,
- Pain from other non-neurological sources.
The Bowstring Test enhances the specificity of the straight leg raising examination. Many patients experience posterior thigh discomfort during SLR due to hamstring tightness, which can be mistaken for radicular pain. The Bowstring Test helps differentiate these conditions:
- Hamstring tightness: Pain during SLR is relieved by knee flexion and is NOT reproduced by popliteal pressure.
- True radiculopathy: Pain during SLR is relieved by knee flexion but IS reproduced by popliteal pressure on the sciatic nerve.
References & More
- Deyerle WM, May VR. Sciatic tension test. South Med J. 1956;49:999–1005. PubMed
- Accident Compensation Corp. New Zealand Acute Low Back Pain Guide. Wellington, New Zealand: New Zealand Guidelines Groups; 2004.
- Cram RH. A sign of sciatic nerve root pressure. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1953;35:192–195.