The Bicipital Aponeurosis Flex Test is used to assess the integrity of the bicipital aponeurosis when evaluating suspected distal biceps tendon ruptures. In cases where the distal biceps tendon is completely ruptured (third-degree strain), the bicipital aponeurosis may remain intact, effectively “masking” the rupture by providing structural support to the biceps muscle and maintaining its normal appearance and length.
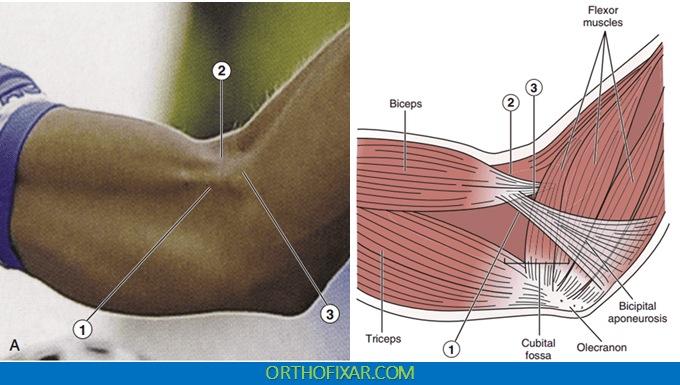
The bicipital aponeurosis is a broad, flat tendinous expansion that arises from the medial border of the biceps brachii tendon at the elbow. It extends medially across the antecubital fossa and blends with the deep fascia of the forearm. This anatomical relationship is crucial because an intact aponeurosis can compensate for a ruptured distal biceps tendon, leading to potential misdiagnosis if not properly evaluated.
How to perform the Bicipital Aponeurosis Flex Test?
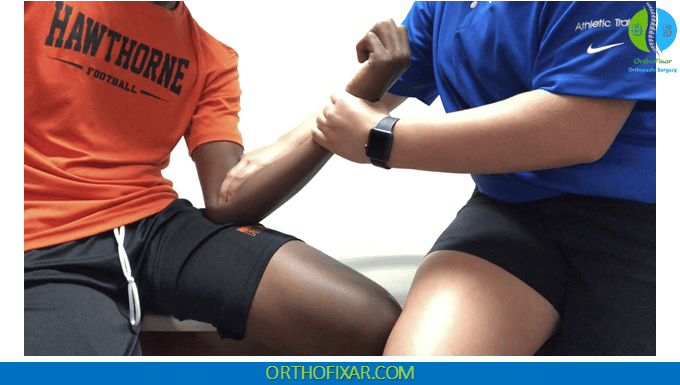
The examination is performed with the patient in a seated position to ensure comfort and optimal positioning. The affected elbow should be flexed to 75 degrees, which positions the bicipital aponeurosis optimally for palpation and tension application.
The patient is instructed to form a tight fist and actively flex both the fingers and wrist while maintaining the forearm in a supinated position. The examiner may provide isometric resistance against the patient’s forearm with one hand to enhance the tensing effect on the aponeurosis. This combined action of wrist and finger flexion with resistance creates tension throughout the bicipital aponeurosis, making it more readily palpable.
See Also: Distal Biceps Tendon Tear
While the aponeurosis is under this induced tension, the examiner systematically palpates three distinct areas of the antecubital fossa: the medial aspect, the lateral aspect, and finally the central portion. This methodical approach ensures comprehensive evaluation of the anatomical structures.
Bilateral comparison is essential for accurate interpretation of this test. The unaffected arm should always be examined using the identical technique to establish a baseline for normal anatomical findings in that particular patient. Individual anatomical variations can influence the palpable characteristics of these structures, making comparative assessment crucial for diagnostic accuracy.
What is the positive Bicipital Aponeurosis Flex Test?
In cases where the bicipital aponeurosis remains intact, the examiner will palpate a characteristic sharp, thin edge of the aponeurosis along the medial aspect of the antecubital fossa. Simultaneously, on the lateral side, the intact biceps tendon should be palpable as a thick, round, cord-like structure. The presence of both these structures indicates continuity of the distal biceps complex.
When a distal biceps tendon rupture has occurred, there will be a distinct palpable gap between the medial aponeurotic edge and the lateral biceps tendon. This gap represents the site of tendon disruption and is the key pathological finding that confirms the diagnosis of distal biceps rupture.
Bicipital Aponeurosis Flex Test Reliability
The Bicipital Aponeurosis Flex Test demonstrated:
- Sensitivity: 100%
- Specificity: 90%
- Diagnostic accuracy: 94%
The Bicipital Aponeurosis Flex Test is a reliable and accurate clinical tool for evaluating BA integrity. It enhances diagnostic confidence in DBTR cases, especially when tendon contour or migration signs are unclear.
The Bicipital Aponeurosis Flex Test should be incorporated into a comprehensive examination of suspected distal biceps injuries such as Ruland Biceps Squeeze Test, alongside other clinical tests and imaging studies as indicated. The results of this test, combined with patient history, mechanism of injury, and other physical examination findings, contribute to the overall diagnostic assessment and treatment planning for patients with potential distal biceps pathology.
References & More
- ElMaraghy A, Devereaux M. The “bicipital aponeurosis flex test: evaluating the integrity of the bicipital aponeurosis and its implications for treatment of distal biceps tendon ruptures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22(7):908–914. Pubmed
- Orthopedic Physical Assessment by David J. Magee, 7th Edition.