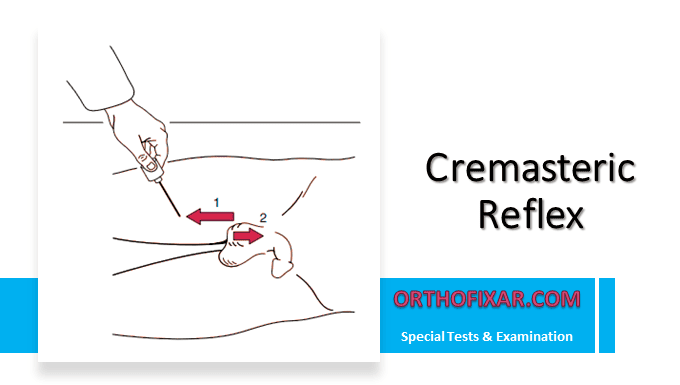
The cremasteric reflex is a superficial reflex that occurs only in males. It provides valuable clinical information about the integrity of the L1–L2 spinal segments and the genitofemoral nerve.
The cremasteric reflex is particularly useful in assessing neurological function:
- Absent or reduced bilaterally: may indicate an upper motor neuron lesion.
- Absent unilaterally: suggests a lower motor neuron lesion affecting the L1–L2 spinal segments or the genitofemoral nerve on that side.
- The absence of this reflex gains additional significance if associated with increased deep tendon reflexes, further supporting the presence of an upper motor neuron lesion.
Related Anatomy
The cremaster muscle is a paired structure made of thin layers of striated and smooth muscle. The muscle has 2 parts, a lateral and medial cremaster muscle. The lateral muscle originates from the internal oblique muscle and inguinal ligament, and the medial cremaster muscle usually originates from the pubic tubercle but sometimes from the lateral pubic crest. The muscles that are covered by a fascia loop over the spermatic cord and testicles and insert into the testicle tunica vaginalis. In the female, the cremaster muscle is found on the round ligament.
The innervation for the cremasteric reflex is provided by the sensory and motor fibers of the genitofemoral nerve that originates from the L1 and L2 spinal nerve nuclei.
See Also: Lumbar Plexus Anatomy
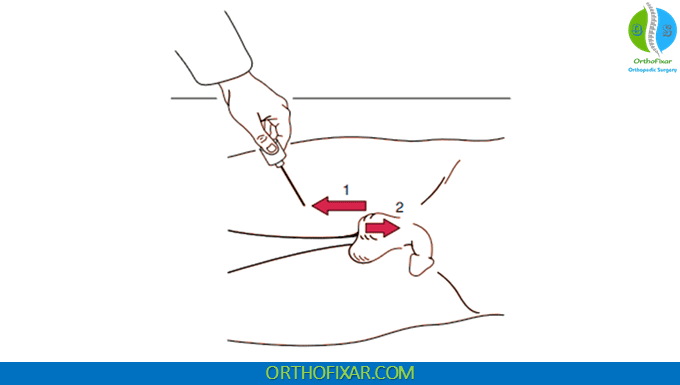
How to Perform the Cremasteric Reflex?
- The patient lies supine and relaxed
- The examiner gently strokes the inner side of the upper thigh using a pointed object (such as the handle of a reflex hammer or a tongue depressor).
See Also: Deep Tendon Reflex Testing
What is the Positive Cremasteric Reflex?
A normal or positive response is a contraction of the cremaster muscle, which causes the scrotal sac on the tested side to elevate. This reaction occurs because of a reflex arc involving:
- Afferent limb: the femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve (L1)
- Efferent limb: the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve (L2)
Bilateral absence or reduction of the cremasteric reflex may suggest:
- An upper motor neuron (UMN) lesion, which could indicate damage to the brain or spinal cord above the reflex arc
Unilateral absence (missing on only one side) may suggest:
- A lower motor neuron (LMN) lesion affecting the nerve roots between L1 and L2 (first and second lumbar vertebrae)
- This could indicate damage to the peripheral nerves, nerve roots, or anterior horn cells at this level.
References & More
- Hoppenfeld S. Physical Examination of the Spine and Extremities. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts; 1976.
- Orthopedic Physical Assessment by David J. Magee, 7th Edition.
- Mellick LB, Mowery ML, Al-Dhahir MA. Cremasteric Reflex. [Updated 2023 Apr 19]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: PubMed