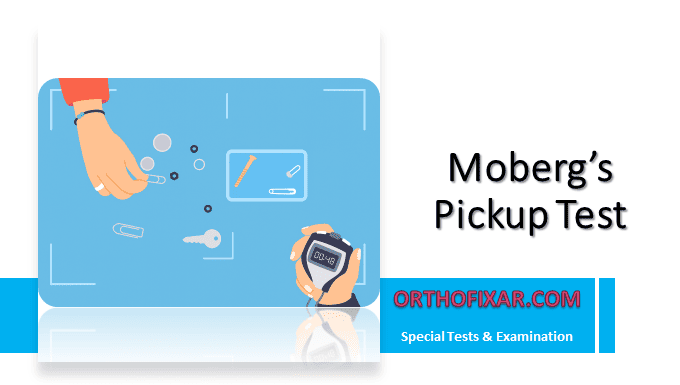
Moberg Pickup Test is a clinical assessment tool designed to evaluate functional sensation in the hand, particularly following median nerve or combined median and ulnar nerve injuries. This test provides valuable insights into how sensory deficits impact fine motor function and object manipulation.
How to Perform the Moberg Pickup Test?
The Moberg Pickup Test requires a collection of 9-10 small objects of varying shapes, sizes, and textures. Standard items include:
- Bolts and nuts
- Screws of different sizes
- Buttons
- Coins
- Pens or pencils
- Paper clips
- Keys
- Small hardware items
These objects should be familiar to the patient and represent items commonly encountered in daily activities. The variety in shape and texture allows assessment of different aspects of tactile discrimination.
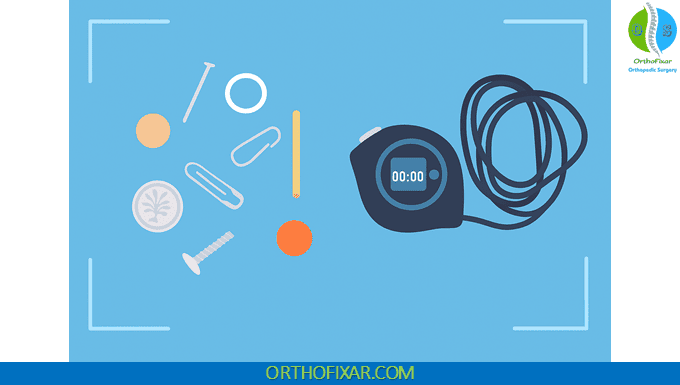
The Moberg Pickup Test examination consists of three distinct phases, each timed separately:
Phase 1: Affected Hand with Vision
The patient uses only the affected hand to pick up objects and place them in a designated container while maintaining visual feedback (eyes are opened). This establishes baseline performance with compensatory visual input.
Phase 2: Unaffected Hand with Vision
The same task is performed with the unaffected hand, providing a control measurement for comparison. This helps distinguish between generalized motor difficulties and specific sensory-related deficits.
Phase 3: Affected Hand without Vision
The patient repeats the task with the affected hand while their eyes are closed, eliminating visual compensation. This phase most directly tests functional sensation and reveals the true impact of sensory loss on hand function.
See Also: Hand Function Tests
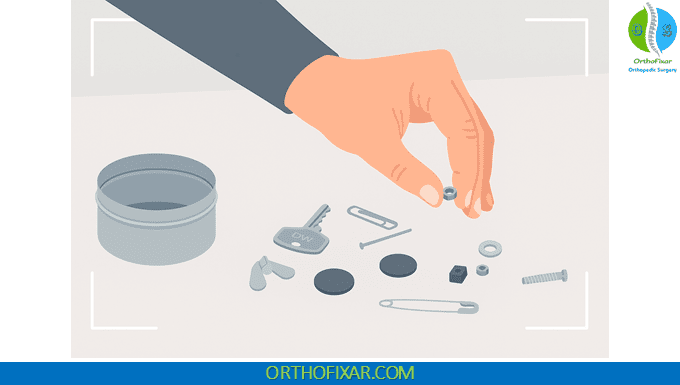
Clinical Observations
During each phase of the Moberg Pickup Test, the examiner carefully observes and documents:
Digit Usage Patterns: Which specific fingers and thumb are actively used for grasping and manipulation. Digits with compromised sensation are typically avoided or used less effectively.
Prehension Strategies: How the patient adapts their grip patterns to compensate for sensory deficits. This may include using different finger combinations or relying more heavily on unaffected digits.
Task Completion Time: Quantitative measurement allows objective comparison between conditions and tracking of recovery progress.
Clinical Applications
Primary Indications
- Median nerve lesions: Particularly valuable for assessing thumb and index finger sensation
- Combined median and ulnar nerve injuries: Comprehensive evaluation of hand sensation
- Post-surgical monitoring: Tracking recovery following nerve repair procedures
- Disability assessment: Objective documentation of functional limitations
Interpretation Principles
The Moberg Pickup Test reveals functional deficits that may not be apparent through traditional sensory testing methods like two-point discrimination or monofilament testing. A significant increase in completion time when vision is eliminated suggests meaningful sensory impairment affecting daily function.
Patients with intact sensation typically show minimal time differences between visual and non-visual conditions, while those with sensory deficits demonstrate marked prolongation when visual cues are removed.
Clinical Significance
Moberg Pickup Test bridges the gap between traditional sensory examination findings and real-world functional capacity. It provides clinicians with objective data about how sensory deficits translate into practical limitations, informing treatment decisions and rehabilitation planning.
The test’s emphasis on functional tasks makes it particularly valuable for assessing occupational capacity and guiding return-to-work decisions in patients whose livelihoods depend on fine manual dexterity.
This assessment tool exemplifies the importance of functional testing in neurological examination, demonstrating how sensory deficits impact the complex integration of tactile feedback, motor control, and cognitive adaptation required for skilled hand function.
References & More
- Callahan AD. Sensibility testing. In: Hunter J, Schneider LH, Mackin EJ, et al., eds. Rehabilitation of the Hand: Surgery and Therapy. St Louis: CV Mosby; 1990.
- Orthopedic Physical Assessment by David J. Magee, 7th Edition.